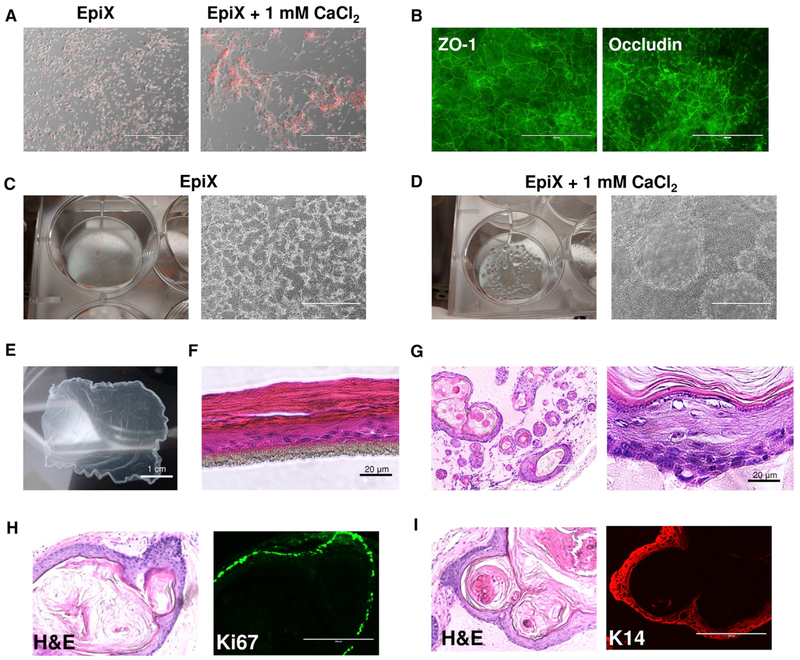
Figure 4. Differentiation of HFKs Expanded with the EpiX Medium.
(A) Addition of 1 mM CaCl2 to the EpiX medium induced the HFKs to differentiate in 24 hr.
(B) Immunofluorescence staining of tight junctions (ZO-1 and Occludin) in HFKs cultured in EpiX plus 1 mM CaCl2 for 7 days. ZO-1, zonula occludens-1.
(C and D) Confluent HFKs in EpiX (C) or EpiX plus 1 mM CaCl2 (D). Many domes with liquid accumulated underneath occurred in the culture with EpiX plus 1 mM CaCl2.
(E) HFKs cultured in a T-75 flask in EpiX plus 1.5 mM CaCl2 for 7 days form an intact epithelium sheet, which was released from the flask after 30-min incubation in dispase at 37°C.
(F) HFKs were differentiated at ALI for 14 days and formed a stratified epithelium.
(G) EpiX-expanded HFKs were subcutaneously injected into immune-comprised mice. After 5 weeks, the cells formed cysts which resembled epidermis.
(H) Most cells in the basal layer were stained positive for the proliferation marker Ki67.
(I) The basal and supra-basal layers of the cystic epithelium stained positive for KRT14 (K14).