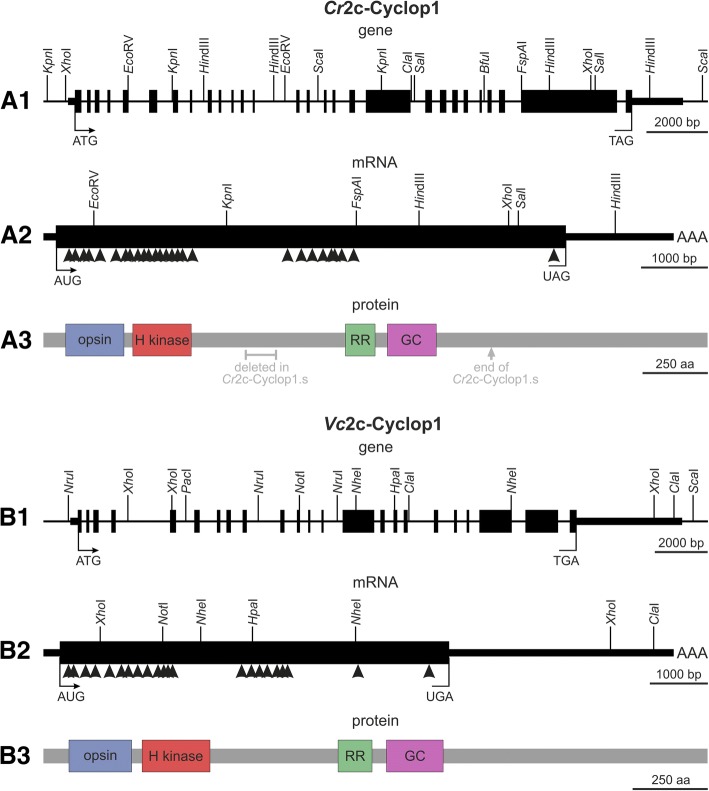
Fig. 1.
Gene structures, mRNA structures, and protein domain compositions of Cr2c-Cyclop1 and Vc2c-Cyclop1. A1, B1. The genetic maps of Cr2c-Cyclop1 and Vc2c-Cyclop1 genes show all exon and intron segments and a number of restriction enzyme cleavage sites. ATG, the translation start site; TAG or TGA, the translation stop site; the filled boxes represent exons; thick horizontal bars indicate untranslated regions; and the thinner horizontal bars represent upstream and downstream sequences. A2, B2. Arrowheads indicate the position of the numerous introns within the genetic maps of the Cr2c-Cyclop1 and Vc2c-Cyclop1 mRNAs. The specified restriction enzyme cleavage sites facilitate orientation. AUG, the translation start site; UAG or UGA, the translation stop site; filled black box, the open reading frame; thick horizontal bar, the 5′- and 3′-UTRs; AAA, the poly A tail. A3, B3. Cr2c-Cyclop1 and Vc2c-Cyclop1 protein domain compositions. Opsin, the rhodopsin domain; H kinase, the histidine kinase domain; RR, the response regulator domain; GC, the guanylyl cyclase domain. Gray text in A3 shows where Cr2c-Cyclop has been shortened to produce Cr2c-Cyclop1