Table 9.
Redox potentials (V vs. NHE) of N-aryl hydroxylamines, hydroxyamic acids, and other acyclic N-hydroxy derivatives as determined by CV or differential pulse voltammetry. Measurements were conducted in phosphate buffer (pH 6).250
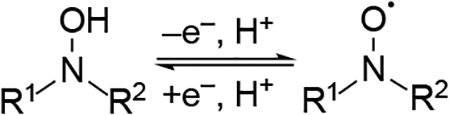
| Entry |
N-Hydroxy Derivatives |
E1/2 | Entry |
N-Hydroxy Derivatives |
E1/2 | Entry |
N-Hydroxy Derivatives |
E1/2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |
0.721 | 7 | 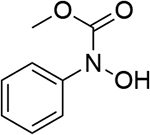 |
0.687 | 13 | 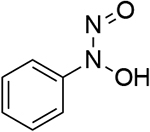 |
0.680 |
| 2 | 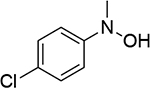 |
0.723 | 8 | 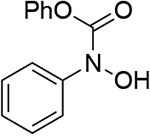 |
0.740 | 14 | 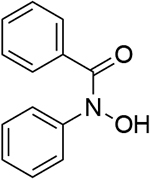 |
0.730 |
| 3 | 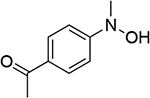 |
0.745 | 9 | 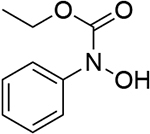 |
0.679 | 15 |  |
0.700 |
| 4 | 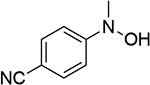 |
0.753 | 10 | 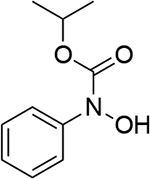 |
0.676 | 16 | 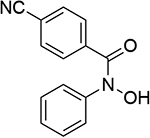 |
0.750 |
| 5 | 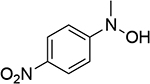 |
0.759 | 11 | 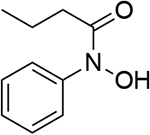 |
0.709 | 17 | 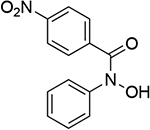 |
0.730 |
| 6 | 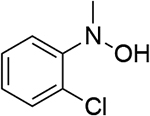 |
0.803 | 12 | 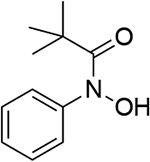 |
0.720 | 18 | 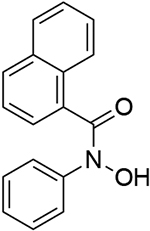 |
0.740 |
