Figure 2.
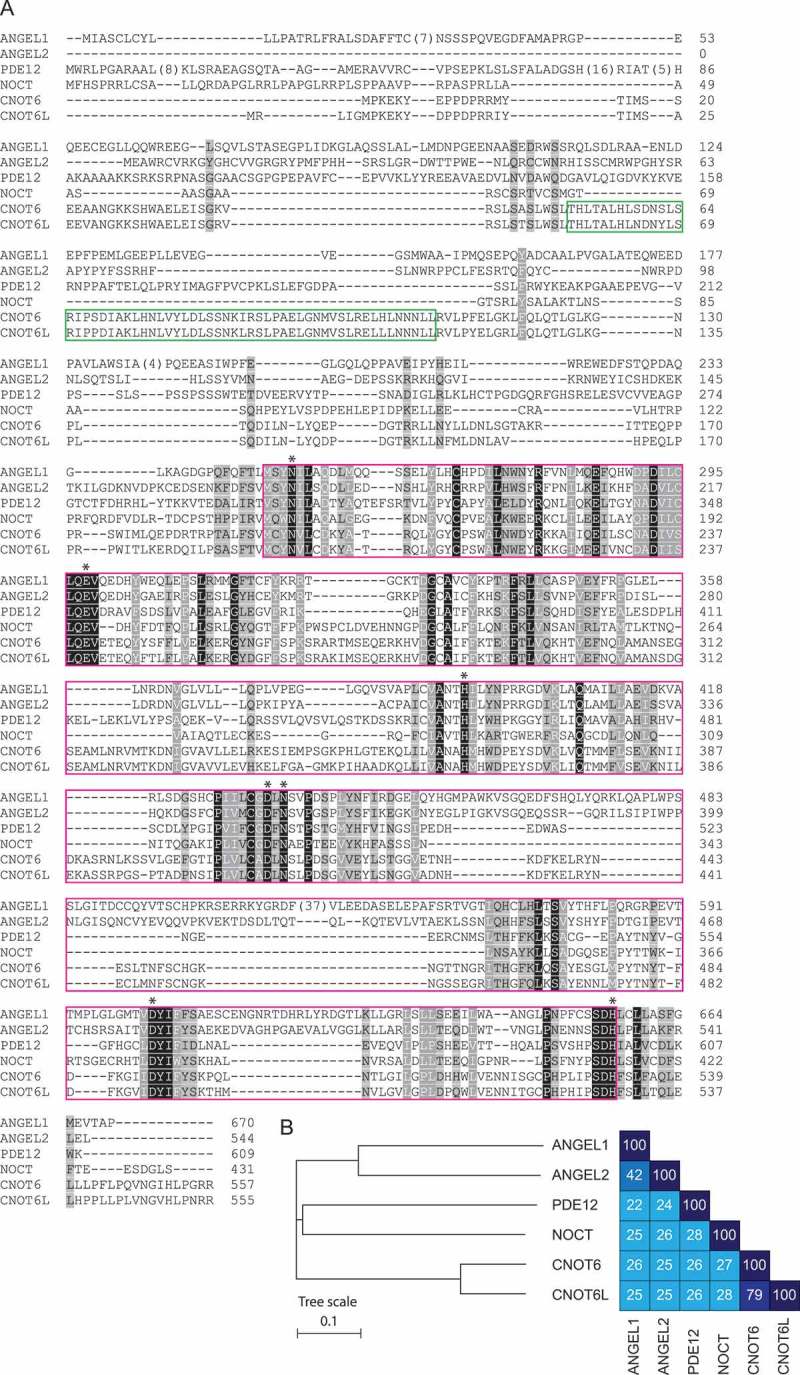
NOCT is related to CCR4-type deadenylases and contains a conserved EEP catalytic domain. A) Multiple sequence alignment of human CCR4-type deadenylases. The shared characteristic EEP domain is boxed in pink; leucine-rich repeats found in CNOT6 and CNOT6L (boxed in green) are absent from NOCT. Putative NOCT catalytic residues (*) are conserved among EEP family members. Amino acid sequences were aligned using Clustal Omega and colored according to extent of chemical property similarity (charge, hydrophobicity, etc.) using Chroma [107,108]. Darker background shading indicates greater similarity, with strictly conserved positions indicated by black background and white text. Uniprot accession numbers: ANGEL1 Q9UNK9, ANGEL2 Q5VTE6, PDE12 Q6L8Q7, NOCT Q9UK39, CNOT6 Q9ULM6, CNOT6L Q965LI5. B) Phylogenetic tree demonstrating the relationships between human CCR4-type deadenylases and pair-wise amino acid identities. Phylogenetic relationships were determined using Clustal Omega and visualized using Interactive Tree of Life [107,109].
