Figure 1.
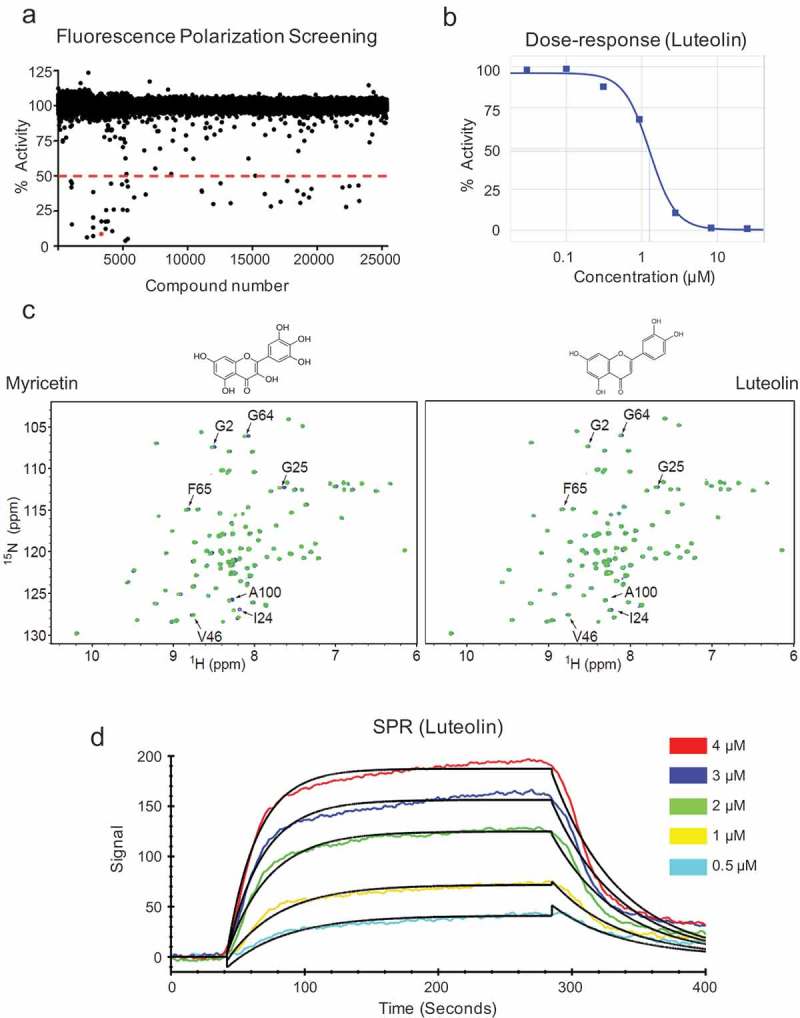
High throughput screen and identification of luteolin as an inhibitor of Msi1. a) Scatterplot displaying the screening results. 25,539 compounds were assayed in a high throughput screen targeting Msi1-RNA interaction. Compounds were tested for inhibition in 7-point dose response study with compounds ranging from 60μM to 8nM. The resulting data were expressed as % activity or the % of bound probe compared to untreated positive control (Msi1 plus Cy3-RNA probe). A 50% activity cutoff was employed to identify potential Msi1 inhibitors. b) Dose-response of luteolin. c) Validation of HTS hits by NMR spectroscopy. 15N HSQC spectra of free Msi1 (green) and Msi1 in the presence of 0.25mM myricetin or luteolin (blue). Chemical shift perturbations affect a subset of Msi1 residues previously shown to be involved in RNA binding. d) Msi1-luteolin interaction by localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR). Representative sensograms for a series of luteolin concentrations (cyan, 0.5μM; yellow, 1μM; green, 2μM; blue, 3μM; red, 4μM) show both the association and dissociation phases of Msi1-luteolin interaction. The black lines represent the fitting of data to 1:1 binding model.
