Figure 6.
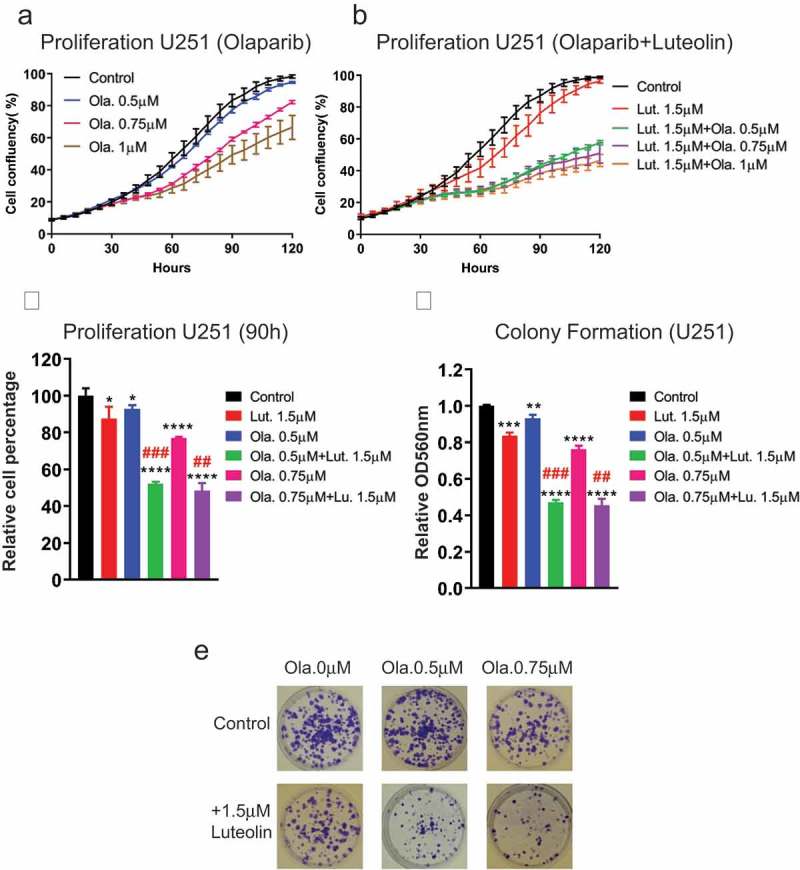
Luteolin sensitizes glioblastoma cells U251 to PARP inhibitor (olaparib). Glioblastoma cells were treated with compounds (luteolin, olaparib or combination of both) and DMSO (control). 48 hours later, the treated cells were harvested and seeded for proliferation and colony formation assays. a,b) The Essen Bioscience IncuCyte automated microscope system was used to follow proliferation of U251 glioblastoma cells over a period of 120 hours. Graphs show cells grew slower in response to combination treatment than olaparib single-treatment. c) The graph shows side by side differences in proliferation between single and combined treatment at 90 hours. d) Graph shows the result of colony formation assay. Colonies were extracted with acidic solution and relative absorbance was measured at 560nm. Combined treatment showed a more pronounced effect on colony formation. e) Colony formation plates were stained with violet blue. Cells treated with olaparib and luteolin produce fewer and smaller colonies in comparison to the ones just exposed to olaparib. All experiments were performed in triplicate. The combination treatment of luteolin and olaparib showed synergistic effect both in proliferation and colony formation, which was judged by the Combination Index (CI) (##CI< 0.9, ###CI< 0.7). Statistical significance was calculated by one-way ANOVA and t test. All data are shown as means ± s.d. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005, ****P < 0.0001).
