Figure 2.
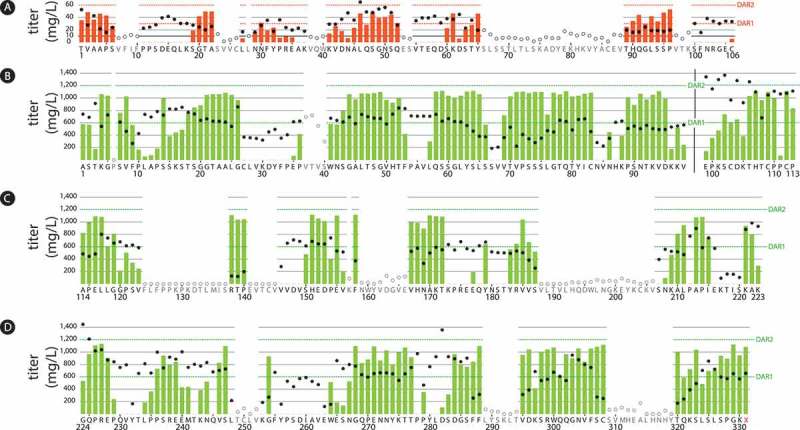
Titers and conjugation results from an aldehyde tag scan of the human kappa light chain and IgG1 heavy chain human IgG1 constant regions.
The aldehyde tag was inserted either after (light chain, Panel A) or before (heavy chain, Panels B-D) each amino acid residue in the constant regions. Tagged antibodies were expressed using a transient system, purified, and conjugated to a cytotoxic payload using a HIPS-functionalized non-cleavable linker. Titers (circles corresponding to the left y-axes) were measured by Protein A on Day 8 post-transfection. Conjugation, reported as drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR) was determined by chromatography. The maximum possible DAR value for each conjugate was 2 (one payload per tagged light or heavy chain). DAR values are indicated as red (light chain) or green (heavy chain) bars corresponding to the right y-axes as follows: Panel A, light chain constant region; Panel B, heavy chain CH1 and hinge domains to the left and right of the black vertical bar, respectively; Panel C, heavy chain CH2 domain; Panel D, heavy chain CH3 domain. In the CH3 region, the heavy chain stop codon is indicated by 331X. Antibodies that expressed poorly or did not bind well to Protein A were not purified or conjugated (open circles denote titers, no DAR values were obtained). Distinct transfection protocols were used to produce the light chain-tagged antibodies (Panel A) and the heavy chain-tagged antibodies (Panels B-D), which accounts for the marked difference in antibody titers and DAR values between the light and heavy chain datasets.
