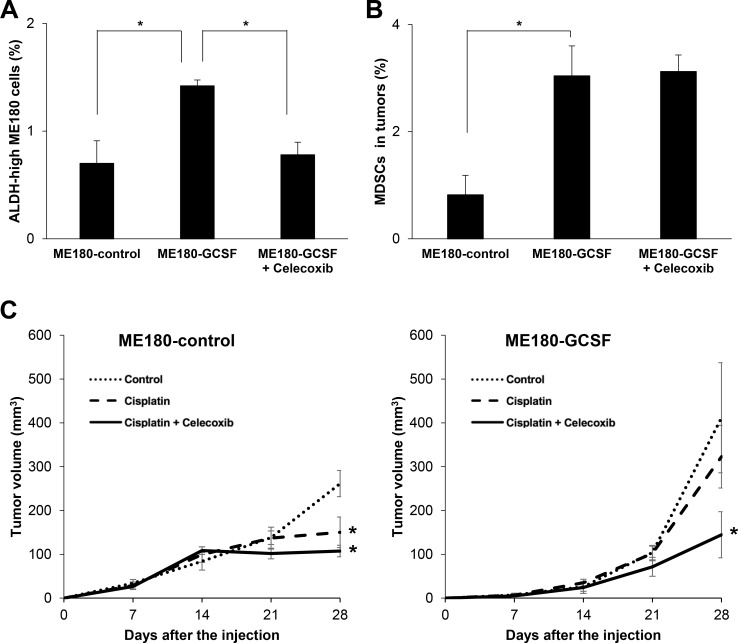
Figure 5. Effects of PGE2-inhibition using with celecoxib.
(A, B) In vivo effect of PGE2-inhibition on the induction of CSCs. Balb/c nude mice were inoculated with ME180-GCSF (n = 10) or ME180-control cells (n = 5). Two weeks after the inoculation, mice bearing ME180-GCSF-derived tumors were randomly assigned to 2 treatment groups: 5 mg/kg of daily celecoxib (i.p.) or PBS. Four weeks after the start of the treatment, their subcutaneous tumors were collected for evaluation. (A) Effect of celecoxib on the induction of CSCs in tumor. The human EpCam+ mouse CD45- cells in the tumors were gated using flow cytometry and then the percentages of ALDH-high cells were assessed using the Aldefluor assay (Bars SD. n = 5, p < 0.01, two-sided Student’s t test). (B) Effect of celecoxib on the induction of MDSCs in tumor. The percentages of MDSCs (CD11b+Gr-1+) in the tumors were assessed using flow cytometry (Bars SD. n = 5, p < 0.01, two-sided Student’s t test). (C) Anti-tumor effect of the celecoxib-mediated inhibition of PGE2-CSC axis in a mouse cervical cancer model. Balb/c nude mice were inoculated with ME180-GCSF or ME180-control cells. Two weeks after the inoculation, the mice were assigned to 4 treatment groups: PBS (n = 5), 5 mg/kg of daily celecoxib (n = 5), 4 mg/kg of weekly cisplatin (n = 5), or 4 mg/kg of weekly cisplatin combined with 5 mg/kg of daily celecoxib (n = 5). The volumes of the tumors were measured for 4 weeks after the inoculation (Bars SD. n = 5, p < 0.05, two-sided Student’s t test).