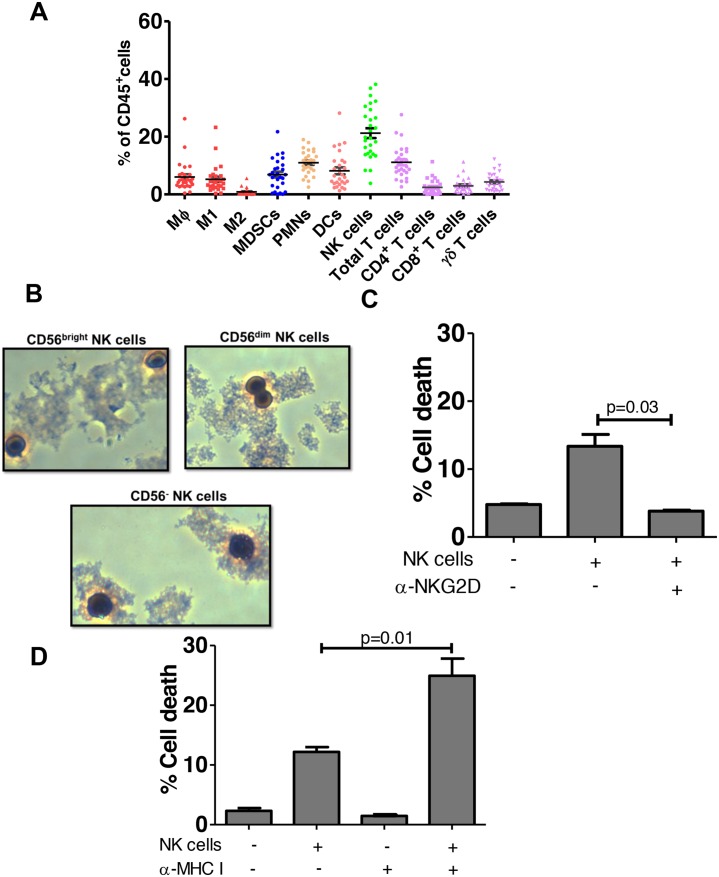
Figure 2. NK cells predominate among bladder intratumoral lymphocytes.
(A) Samples of human bladder tumors in local bladder cancer patient cohort (n=28) were taken at time of cystoscopy/cystectomy. Human lymphocytes were gated as in Figure 1 and plotted as % of CD45+ lymphocytes. MΦ- Macrophages, M1 – M1 macrophages, M2- M2 Macrophages, MDSCs- myeloid derived suppressor cells, PMN-polymorphonuclear cells (neutrophils), DC- dendritic cells, NK - natural killer, APC-Antigen presenting cells. Mean ± SEM. (B) Wright-Giemsa stain of CD56bright, CD56dim and CD56- NK cells isolated from bladder tumor tissue observed under light microscopy (40x magnification). (C) Cytotoxicity assay of sorted NK cells from human bladder tumor with CFSE-labeled K562 target cells in the presence of NKG2D-blocking antibody or an isotype control antibody. p-values represent two-tailed unpaired t-tests. (D) Graphed results of NK cell cytotoxicity assay with sorted NK cells from human bladder tumor with CFSE-labeled RT4 bladder cancer target cells. To block, MHC-I CFSE labeled target cells were incubated with MHC-I blocking antibody prior to addition of the NK cells. p-values represent two-tailed unpaired t-test.