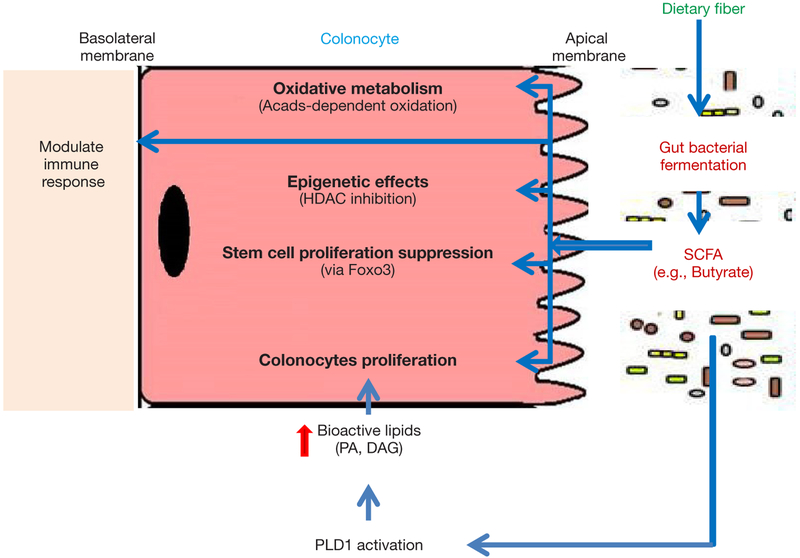
Figure 1.
Model of butyrate-mediated effects on colonocytes. Indigestible dietary fibers (DF) are being fermented by commensal microbial community residing in the large intestine. Butyrate, a major product of DF fermentation, is actively metabolized by colonic crypts through Acads-dependent oxidation and used as energy source. In addition, butyrate exhibit several biological effects such as HDAC inhibition, suppression of colonic epithelial stem/progenitor proliferation, regulation of immune response, and stimulation of colonocyte proliferation via PLD1 activation and generation of bioactive lipids. SCFA, short chain fatty acids; HDAC, histone deacetylase; Acads, Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; Foxo3, Forkhead box O3; PLD1, phospholipase D1; PA, phospahtidic acid; DAG, diacylglycerol.