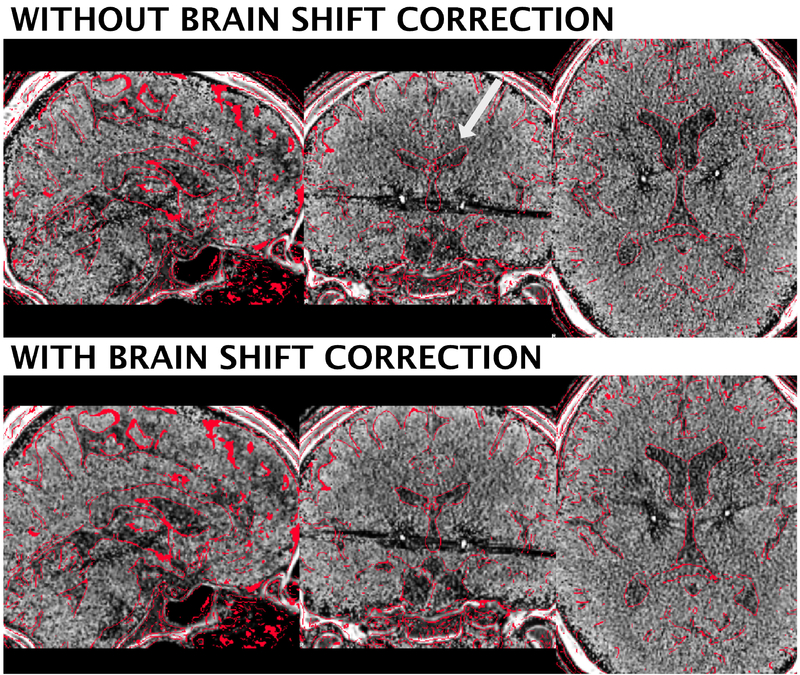
Figure 5:
Brain shift correction results of the 3T example patient. The approach serves as a refinement registration step between post- and preoperative acquisitions and is able to minimize nonlinear registration errors due to pneumocephalus (figure S1). In the present example, the postoperative CT was shifted by 1.66 mm in z-, 0.9 mm in y- and 0.17 mm in x-direction. A better registration can best be seen in the area of the ventricles (white arrow). Postoperative CT was tone mapped to show contrast in both brain and skull windows.