Figure 1. IL-6 is a proinflammatory modulator of T cells.
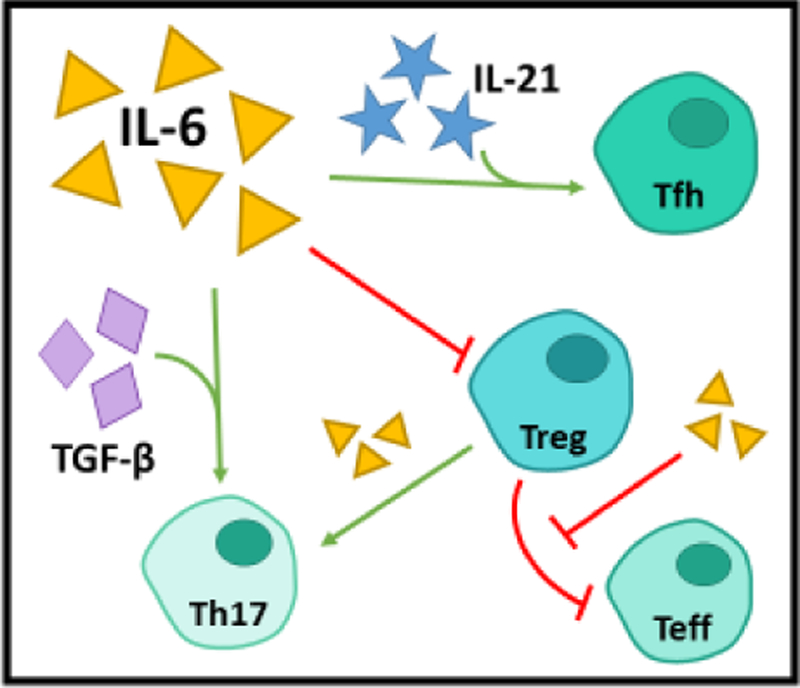
IL-6 contributes to autoimmunity by promoting Tfh, Th17, and Teff lineage and function and by inhibiting the suppressive capacity and induction of Tregs. In the presence of IL-21, IL-6 promotes commitment to the Tfh lineage, which is capable of stimulating B cell proliferation and class switching. In addition to bolstering Teff resistance to suppression by Tregs, IL-6 also promotes the conversion of Tregs to Th17 and may reduce Treg suppressive capacity. Lastly, in the presence of TGF-β, IL-6 enhances commitment and function of Th17 cells, a well-established pathogenic cell type in autoimmunity.
