Figure 4: Peripheral and barrier tolerance mechanisms.
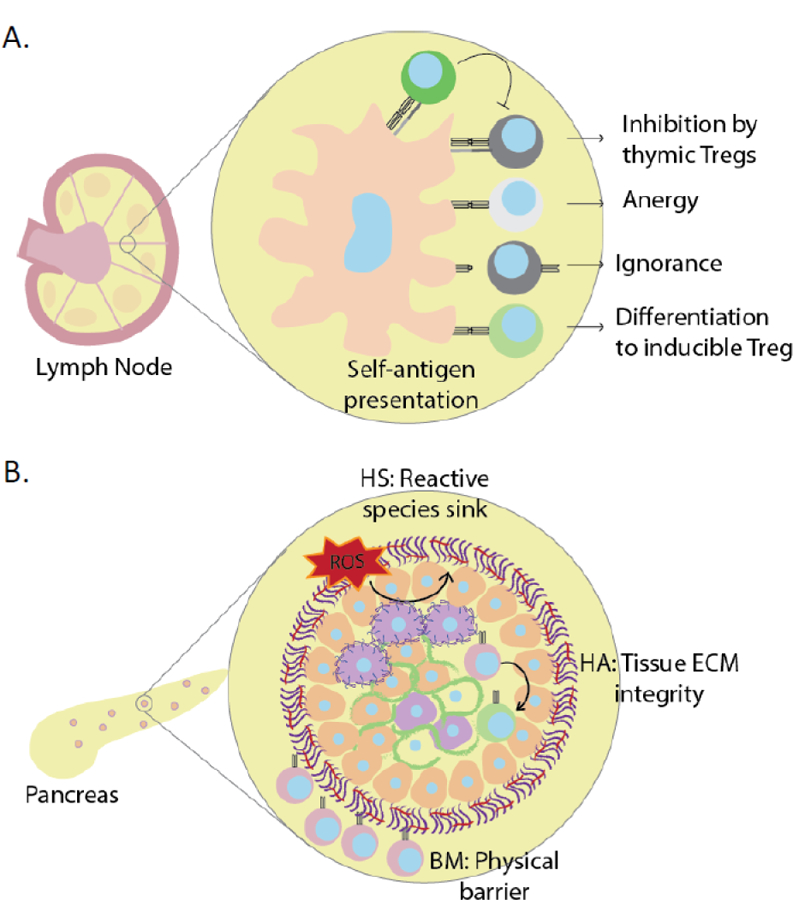
(A) Peripheral tolerance of autoreactive effector T cells is maintained via inhibition by thymic Tregs, induction of anergy, antigenic ignorance, or differentiation to inducible Tregs. (B) The intact islet ECM provides physical and immunologic barriers (“barrier tolerance”) that contribute to immune tolerance. These include a basement membrane that prevents immune infiltration, protective barriers against reactive oxygen species as with HS, and immunomodulatory barriers like the stabilization and sequestration of HA that limit immune activation.
