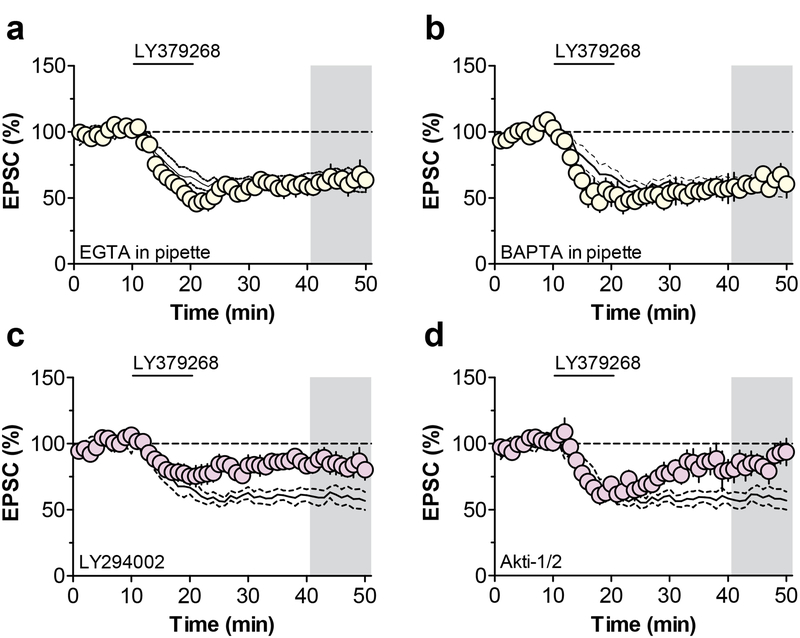
Figure 3. mGlu3-LTD proceeds through PI3K-Akt signaling pathway.
(a) The divalent ion chelator EGTA was added to the patch pipette to quench Ca2+ signaling in the postsynaptic cell. This manipulation had no effect on the expression of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 3 (mGlu3)-dependent long-term depression (LTD) (62.1 ± 6.9% baseline, n/N = 7/4 cells/mice). Black lines in panels 3a-4d represent data from control experiments displayed in panel 1b. (b) The divalent ion chelator BAPTA was added to the patch pipette and did not affect mGlu3-LTD (59.9 ± 4.9% baseline, n/N = 5/3). (c) The phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor LY294002 impaired the expression of mGlu3-LTD (85.7 ± 5.1% baseline, n/N = 8/6). (d) The Akt inhibitor Akti-1/2 blocked mGlu3-LTD (89.6 ± 11% baseline, n/N = 5/4). EPSC, excitatory postsynaptic current; LTD, long-term depression; mGlu3, metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 3; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase.