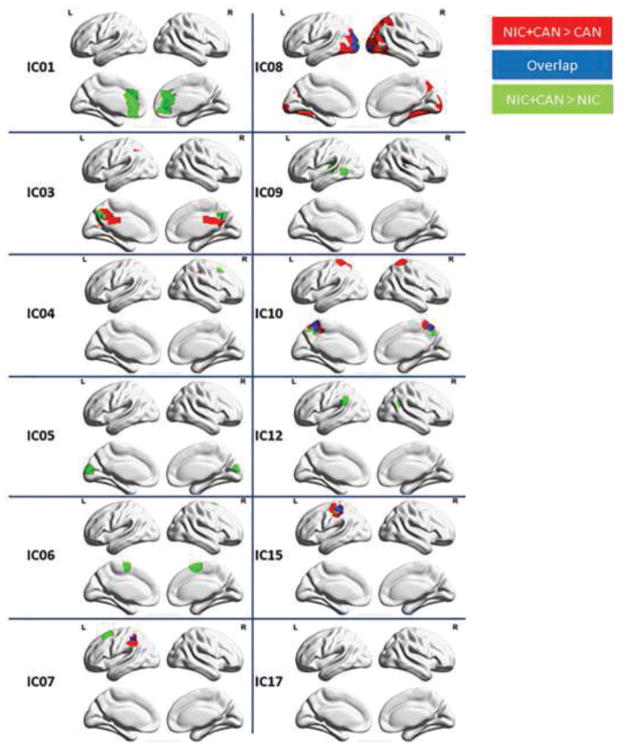
Figure 3. Differences in resting state functional connectivity between substance using groups via t-tests.
Concurrent nicotine and cannabis users (NIC+CAN) exhibited significantly greater connectivity in posterior DMN (IC03), left frontal parietal network (IC04), right frontal parietal network (IC07), higher visual network (IC08), cuneus/precuneus (IC10) and dorsal attention network (IC15) compared to NIC and CAN users. NIC+CAN users also exhibited greater connectivity in the anterior DMN (IC01), lingual gyrus (IC05), salience network (IC06), and insular cortex (IC09) compared to NIC users (p < 0.05, FWE corrected using FSL randomise).