Figure 3. In vivo downregulation of Kcnk13 with lentiviral siRNA.
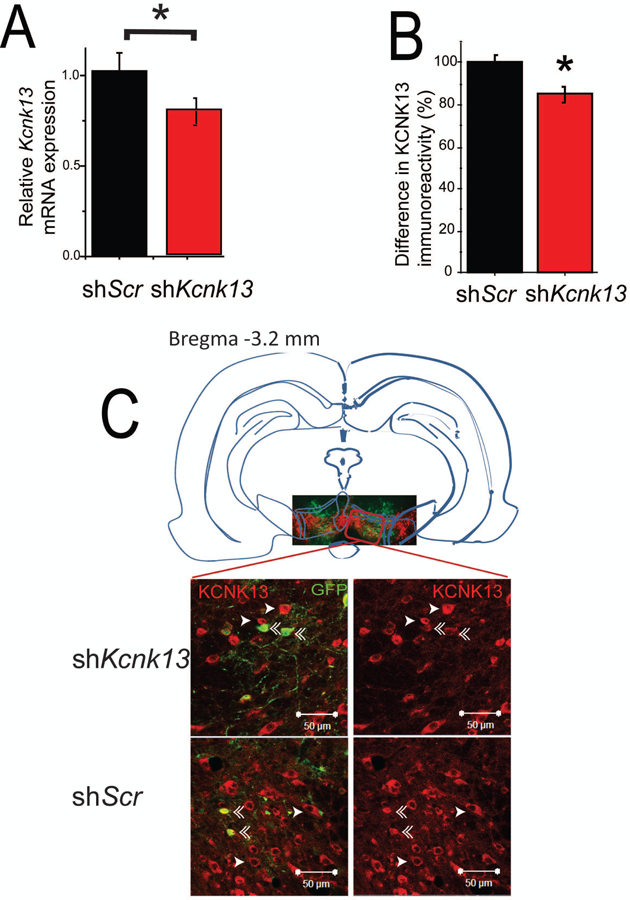
A. Reduced expression of Kcnk13 mRNA in the VTA of mice expressing shKcnk13 compared with mice expressing the control shRNA, shScr. Effectiveness of Kcnk13 shRNA in the VTA was assessed by qPCR of RNA from dissected VTA three weeks after lentivirus infection. Kcnk13 was reduced by 22.2% (unpaired t-test, t-statistic= 1.92,* p< 0.05, n=6).
B, C. Reduced expression of KCNK13 protein in the VTA of mice expressing shKcnk13. Immunohistochemistry was performed three weeks after lentiviral infection using antibodies to KCNK13 and GFP. KCNK13 immunoreactivity was compared between GFP-positive neurons and GFP-negative neurons.
B. GFP-positive neurons in mice expressing shKcnk13 expressed 15.1± 3.4% less KCNK13 immunoreactivity than GFP-negative neurons (paired t-test, t= −4.88, p<0.001, n=18). In mice expressing shScr in the VTA, GFP-positive neurons expressed 0.64 ± 3.4% more KCNK13 immunoreactivity compared to GFP-negative neurons (paired t-test, t= 0.305, p>0.05, n=15). Asterisk (*) indicates significant difference between GFP-positive and GFP-negative neurons.
C. Illustration of the typical location of microinjection sites (inset picture showing VTA region immunostained for GFP and TH) and immunostaining of KCNK13 and GFP in mice expressing shKcnk13 and shScr (four larger pictures). Single arrowhead indicates KCNK13-immunoreactive cells, double arrowhead indicates cells immunoreactive for both KCNK13 and GFP. Note the reduced KCNK13 immunoreactivity in the GFP-immunoreactive cells.
