Fig. 3.
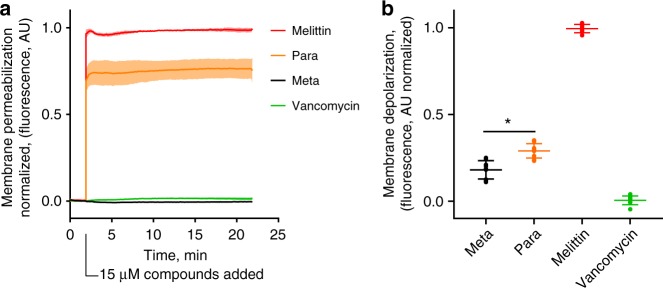
The Meta and Para were distinguishable and active on the bacterial membrane. a Propidium iodide (PI) assay demonstrated the ability of the Para to disrupt and permeabilize the bacterial membrane of MRSA (ATCC 33591) at significantly greater activity than the Meta (p = 0.0015, df = 2.018, unpaired t-test, two-tailed). The shaded region indicates the standard deviation around a solid line (mean) of n = 3 biological replicates with n = 2 technical replicates each. b diSC35 membrane depolarization assay performed against MRSA (n = 3 biological replicates). The Para shows stronger membrane depolarization, (*p < 0.028, df = 3.995, unapaired t-test, two-tailed). In both assays, oligomers and controls were added at 15 μM to compare their activity. Vancomycin inhibits cell wall synthesis and serves as a negative control