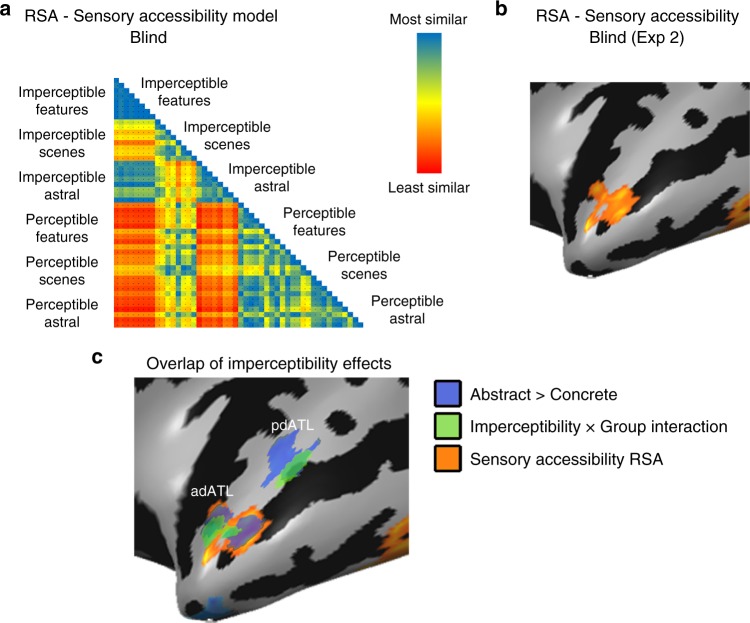
Fig. 3.
Concepts’ Imperceptibility is mapped in left dorsal ATL pattern. a, b Multivariate representational similarity analysis (RSA) was computed comparing a behavioral matrix based on ratings of the blind subjects of the sensory perceptibility of the concepts (a; representational dissimilarity matrix) with the neural patterns in Exp. 2 in a searchlight manner across the brain. Sensory perceptibility correlation (b) was found in the dorsal ATL, overlapping the effects of imperceptibility X group interaction and abstract concepts preference. For additional control RSA analyses see Supplementary Fig. 4. c The main effects from Figs. 1–3 are shown together, to reveal the overlap in the dorsal ATL between preference for abstract concepts (over concrete ones; Fig. 1c; depicted in blue; data from Exp. 1), Imperceptibility X Group interaction (Fig. 2a; depicted in green; data from Exp. 1) and the sensory perceptibility RSA (b; depicted in orange; data from Exp. 2)