Fig. 6.
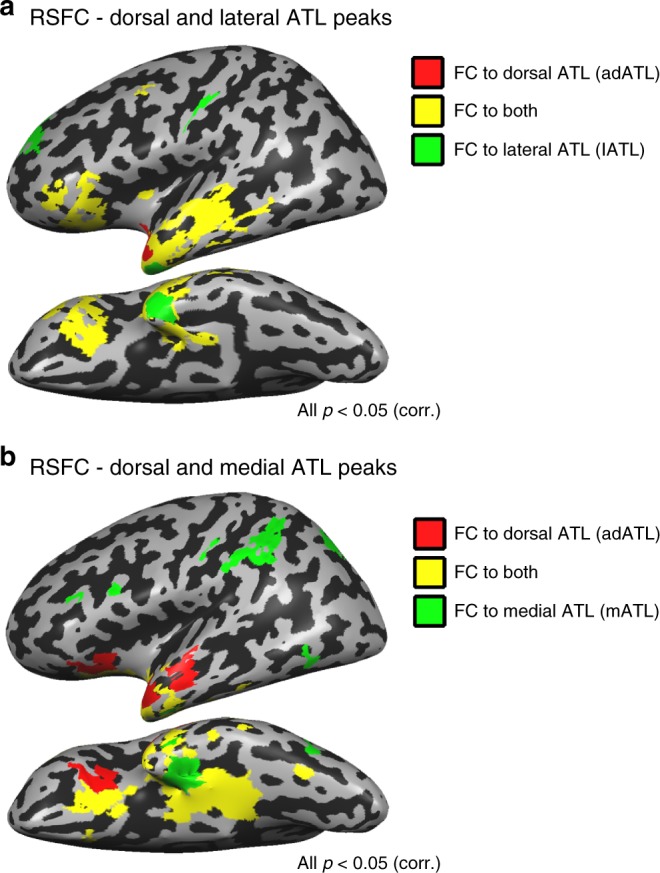
Different functional networks for different aspects of ATL. a Partial RSFC was computed from the dorsal (red; adATL) and lateral (green; lATL) ATL peaks in the sighted. Overlapping RSFC to both seeds (in yellow) is predominant, showing that these two regions belong largely the same functional network. Similar findings were evident in the blind group, and group differences in the connectivity to these seeds were minimal (see Supplementary Fig. 7A,C,D). b The dorsal and medial ATL regions, which show opposite preferences for perceptibility in the blind (adATL and mATL) belong to largely different functional networks in the sighted. Partial RSFC is plotted for the dorsal (red) and medial (green) ATL. Overlapping RSFC to both seeds is depicted in yellow. Similar findings were evident in the blind group, and group differences in the connectivity to these seeds were minimal (Supplementary Fig. 7B,C,E)
