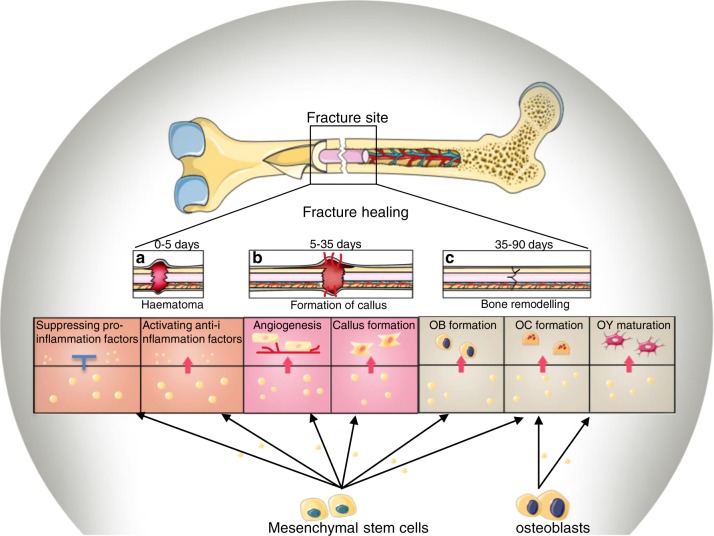
Fig. 6.
Roles of exosomes in fracture healing at different stages. a Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-derived exosomes have anti-inflammation property by upregulating anti-inflammation factor TGF-β and suppressing pro-inflammation factors: TNF-α and IL-1β. Thus, exosomes can be used to prevent over reaction of inflammation-induced delay of fracture healing. b In the stage of callus formation, exosomes act as promoters by enhancing proliferation and differentiation of endothelial cells as well as the formation of fibroblasts. As a result, enhanced angiogenesis and callus formation induced by exosomes can be detected at this stage. c Osteoblast (OB) and MSC-derived exosomes are promoters of bone remodelling. MSC-derived exosomes are suggested to boost the proliferation and liability of OBs. Besides, MSC and OB-derived exosomes are shown to enhance osteoclast (OC) differentiation. OB-derived exosomes are also enhancers of osteocyte (OY) formation by regulating AT-hook 2 (HMGA2) and AXIN2