Fig. 2.
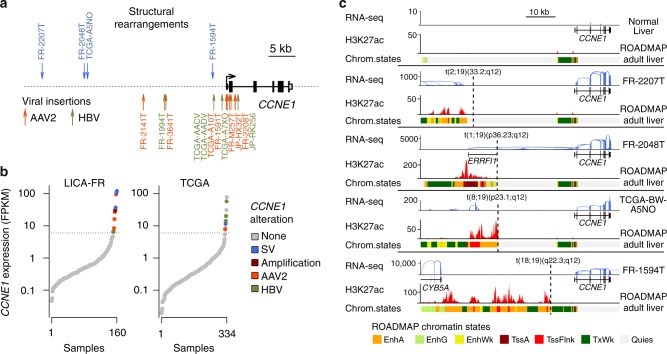
Viral and non-viral mechanisms of CCNE1 activation in HCC. a Summary of structural rearrangements (top) and viral insertions (bottom) affecting CCNE1 gene identified in 751 HCC from the LICA-FR, TCGA and ICGC-JP cohorts. b Sorted CCNE1 expression (log scale) in the LICA-FR and TCGA cohorts. Gene expression was obtained from RNA-seq data and is given in fragments per kilobase of exons per million reads (FPKM). Samples harboring structural variants (SV), focal amplifications and viral insertions are indicated with a color code. c Functional consequences of structural rearrangements affecting CCNE1 regulatory region. RNA-seq read counts along CCNE1 locus are represented in normal liver (top) and in 4 tumors harboring structural rearrangements upstream CCNE1 trancription start site (TSS). H3K27Ac chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) signal and chromatin states in adult liver were obtained from the ROADMAP consortium and are depicted below each reconstruted DNA sequence. EnhA: active enhancer; EngG: genic enhancer; EnhWk: weak enhancer; TssA: active TSS; TssFlnk: flanking TSS; TxWk: weak transcription; Quies: quiescent chromatin