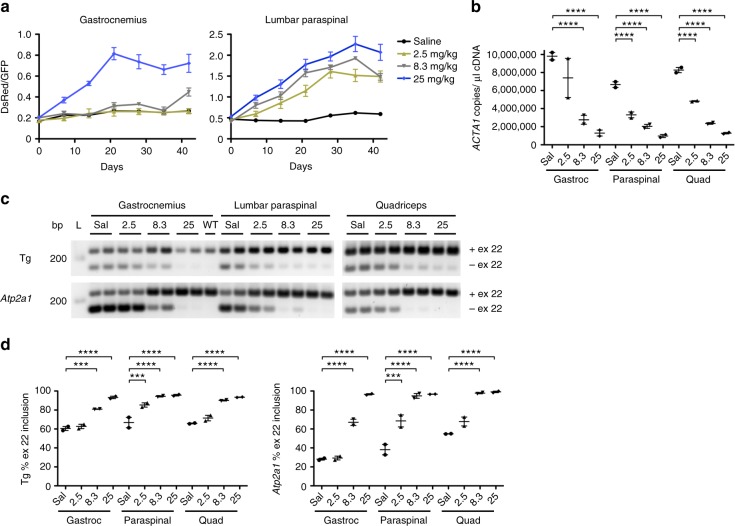
Fig. 6.
In vivo activity of a novel ligand-conjugated antisense (LICA) oligonucleotide. We treated TR;HSALR bi-transgenic mice with saline or a novel LICA oligonucleotide, ASO 992948, targeting ACTA1-CUGexp transcripts and measured DsRed and GFP fluorescence by serial in vivo spectroscopy. LICA-oligo doses were 2.5, 8.3, or 25 mg/kg twice weekly for 4 weeks (8 total doses) by subcutaneous injection (N = 2 each group). However, due to low DsRed/GFP fluorescence measurements in gastrocnemius muscles, mice receiving the 2.5 mg/kg and 8.3 mg/kg doses received four additional injections over the next 2 weeks, for a total of 12 doses. a Serial DsRed/GFP measurements in gastrocnemius and lumbar paraspinal muscles through Day 42. The final dose in the saline (black circles) and 25 mg/kg groups (blue diamonds) was Day 24, while the final dose in the 2.5 (yellow triangles) and 8.3 mg/kg (gray triangles) groups was Day 37. Error bars indicate mean ± s.e.m. b Quantitation of ACTA1-CUGexp transcript levels (copies per microliter cDNA) by droplet digital PCR in muscles collected at Day 42. Error bars indicate mean ± s.e.m. ****P < 0.0001; two-way ANOVA. c Splicing analysis by RT-PCR in gastrocnemius and lumbar paraspinal muscles collected at Day 42. L DNA ladder, bp base pairs. d Quantitation of splicing results in c. Error bars indicate mean ± s.e.m. ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001; two-way ANOVA