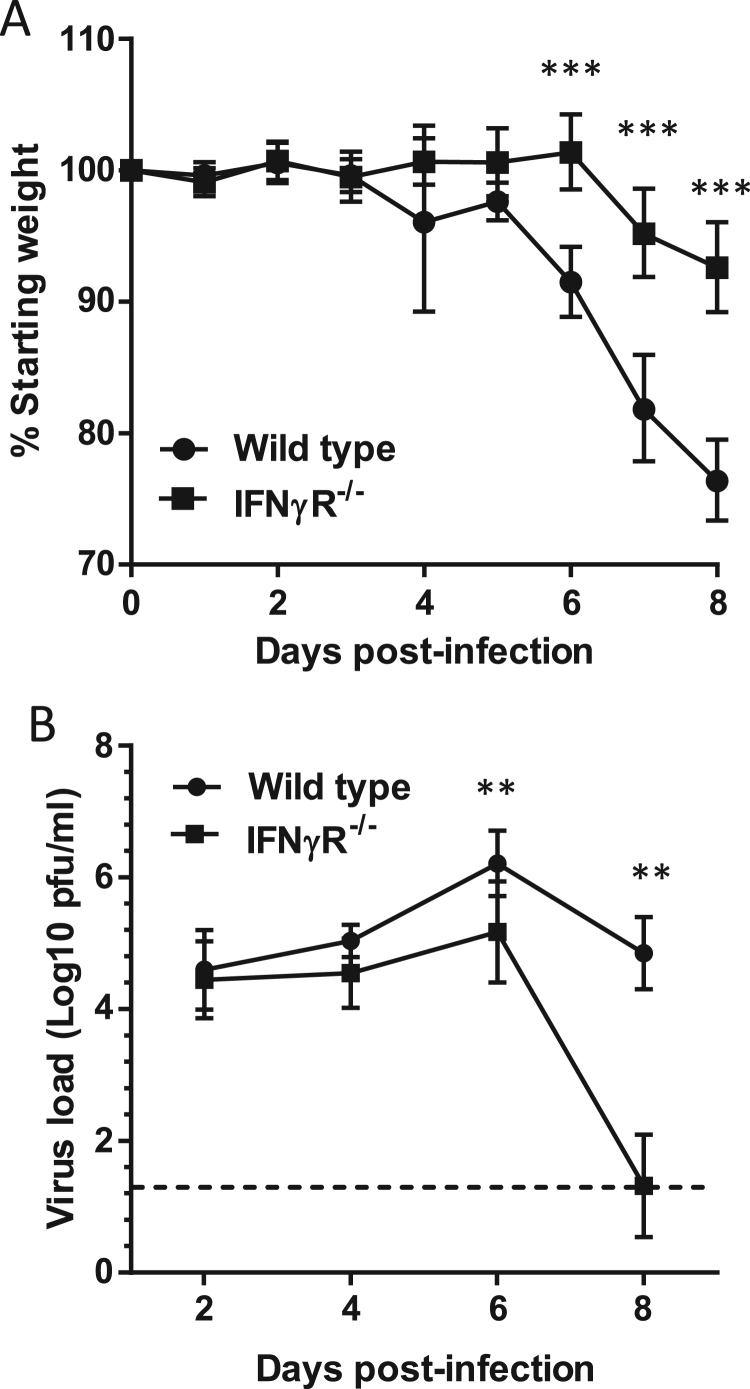
Fig. 1.
IFNγR-/-mice are more resistant to severe IAV infection than wild type mice. Wild type and IFNγR-/- mice were infected with A/WSN/33 and monitored daily for weight loss (A); at appropriate time points, lungs were harvested and assayed for infectious virus (B). Graphs show mean with 95% CI, data are from 6 experiments in total with between 29 (weight day 0 wild type) and 6 (days 7–8 IFNγR-/-) mice per time point. Data were analysed by ANOVA, with experiment added as a fixed effect for days 1–4. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01.