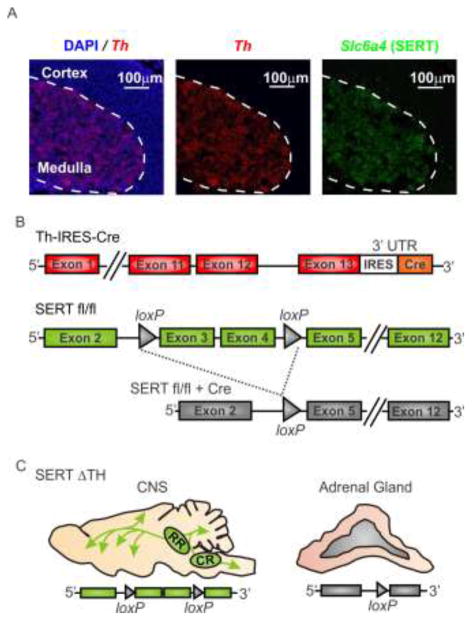
Figure 1. Strategy to generate conditional knockout of SERT in the sympathoadrenal system.
A) A multicolor in situ hybridization approach (RNAscope) was used to confirm co-expression of Slc6a4 (SERT) and tyrosine hydroxylase (Th), the rate-limiting enzyme for catecholamine biosynthesis, in the adrenal medulla. The merged image (left) shows Th (red) mRNA expression and DAPI-labeled nuclei (blue) in an adrenal gland section from a wild-type mouse. Th is expressed in chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla but is absent from the adrenal cortex. The dashed line in all images indicates the demarcation of the adrenal medulla and cortex as defined by Th expression. In the same section, the Slc6a4 mRNA (SERT; green, right image) expression pattern is similar to Th and is restricted to the adrenal medullary chromaffin cells. B) Schematic representation of the strategy to conditionally excise the floxed SERT gene (SERTfl/fl) by Cre-mediated recombination. Th-IRES-Cre is a knock-in mouse with Cre inserted into the 3′-untranslated region (UTR) of tyrosine hydroxylase (Th) (upper panel). In the floxed SERT mouse (SERTfl/fl), loxP sites flank exons 3 and 4 of the Slc6a4 gene (middle panel). Cre-mediated recombination results in functional knockout of Slc6a4 (SERT) by excision of exons 3 and 4 (lower panel). C) SERTΔTH conditional knockout mice were generated by crossing SERTfl/fl with Th-IRES-Cre mice (for more detail see methods section 2.2). The illustration shows the predicted tissue specific excision of SERT from the adrenal gland but not the CNS of the SERTΔTH mice.