Figure 4. Endogenous midbrain 5-HT homeostasis was maintained in SERTΔTH mice.
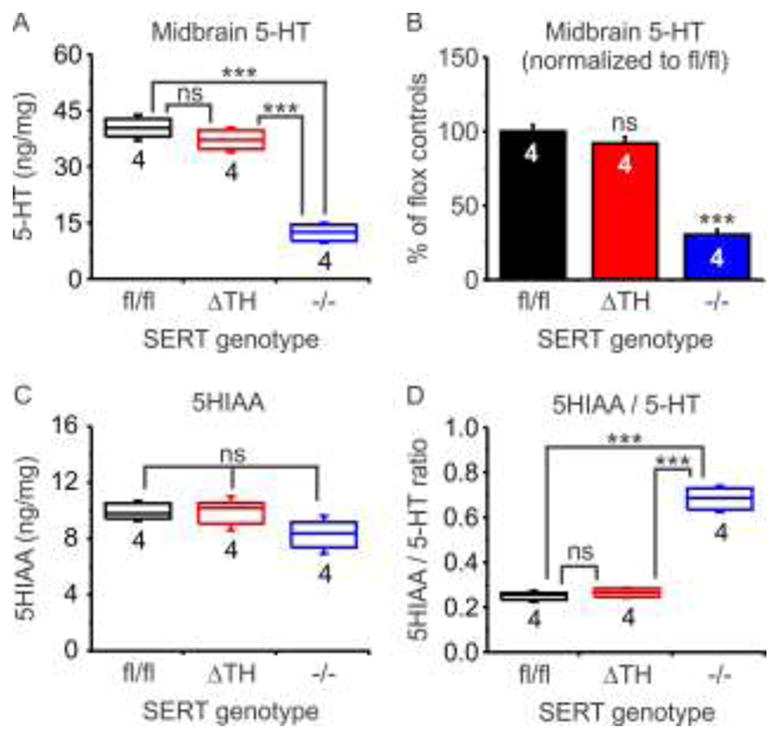
The amounts of endogenous 5-HT and its metabolite 5-HIAA were determined in midbrain tissue from SERTΔTH mice (n = 4), SERTfl/fl littermates (n = 4), and SERT−/− mice (n = 4) using HPLC and normalized to total protein content of the samples (ng / mg protein). Also shown is the 5-HIAA / 5-HT ratio that can be used as an indicator of 5-HT turnover. Box plots indicate the median with interquartile range and whiskers denote standard deviation. The number of biological replicates (n values) is indicated below the boxes. Statistical comparison was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-test for multiple pairwise comparisons. A) 5-HT content was not different in SERTΔTH and SERTfl/fl but was significantly reduced in SERT−/− (F = 94, P < 0.0001; ns, not significantly different, P = 0.55; *** P < 0.0001). B) Same data as in panel A is expressed as a percentage of the mean value detected in SERTfl/fl mice (F = 94, P < 0.0001; ns, not significantly different, P = 0.55; *** P < 0.001). C) 5-HIAA content was not significantly different across genotypes (F = 2.75, P = 0.12). D) Turnover of 5-HT assessed as the ratio of 5-HIAA / 5-HT was not significantly different in SERTΔTH and SERTfl/fl but was enhanced in SERT−/− (F = 162, P < 0.0001; ns, not significantly different, P = 1; *** P < 0.0001).
