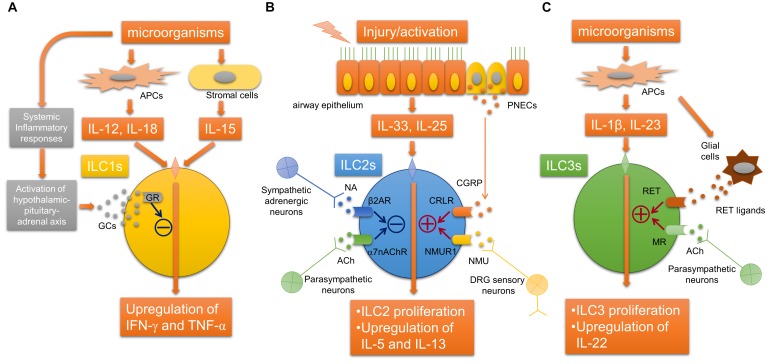
FIGURE 2.
Neuroimmune interaction regulating innate lymphoid cells. (A) Glucocorticoids derived from hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis stimulated by inflammatory mediators during systemic inflammation bind to GRs in ILC1s, which inhibits the release of IFN-γ. (B) The activation of ILC2s by epithelial alarmin cytokines is inhibited by ACh derived from parasympathetic neurons and possibly non-neuronal cells via α7nAChR, or NA derived from sympathetic neurons via β2AR. In contrast, neuromedin U derived from DRG sensory neurons or CGRP derived from PNECs augments the activation of ILC2s via NMUR1 or CRLR, respectively. (C) RET ligand derived from glial cells or acetylcholine derived from parasympathetic neurons arguments the proliferation and activation ILC3s via RET or muscarinic receptors, respectively. α7nAChR, α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; ACh, acetylcholine; APC, antigen-presenting cell; β2AR, beta-2 adrenergic receptor; CGRP, calcitonin gene-related peptide; CRLR, calcitonin receptor-like receptor; DRG, dorsal root ganglia; GCs, glucocorticoids; IFN-γ, interferon-gamma; ILCs, innate lymphoid cells; MR, acetylcholine muscarinic receptor; NA, norepinephrine; NMU, neuromedin U; NMUR1, neuromedin-U receptor 1; PNEC, pulmonary neuroendocrine cell; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha.