Fig. 1.
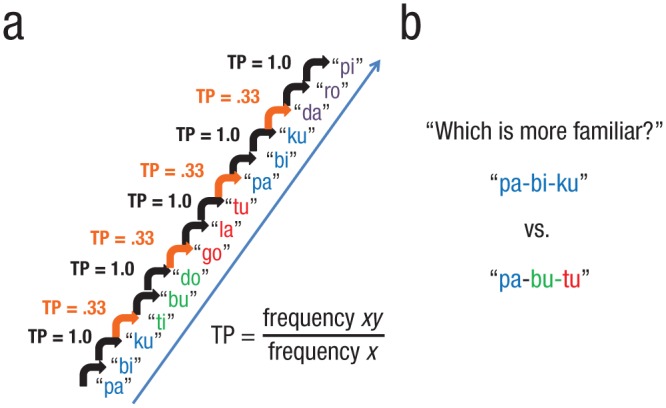
Triplet task (Saffran, Aslin, & Newport, 1996). In the familiarization phase, a portion of which is shown here (a), participants are given passive exposure to a continuous sequence of individually presented stimuli that co-occur to form triplets. There are differences in the transitional probability (TP) of stimuli within versus across triplet boundaries (e.g., TP = 1.0 vs. TP = .33). The formula for TP is provided, which gives the conditional probability of a given item (y) occurring following the occurrence of (x).The subsequent test phase (b) is comprised of two-alternative forced-choice trials requiring participants to judge which of two sets of triplets is familiar. On each trial, one triplet is consistent with the co-occurring stimuli presented during the familiarization phase, whereas the other is a foil triplet. In the figure, colors are used to illustrate which syllables are part of which triplets. This task is sometimes referred to as word segmentation or speech segmentation because the original task utilized spoken (nonsense) syllables.
