Figure 7.
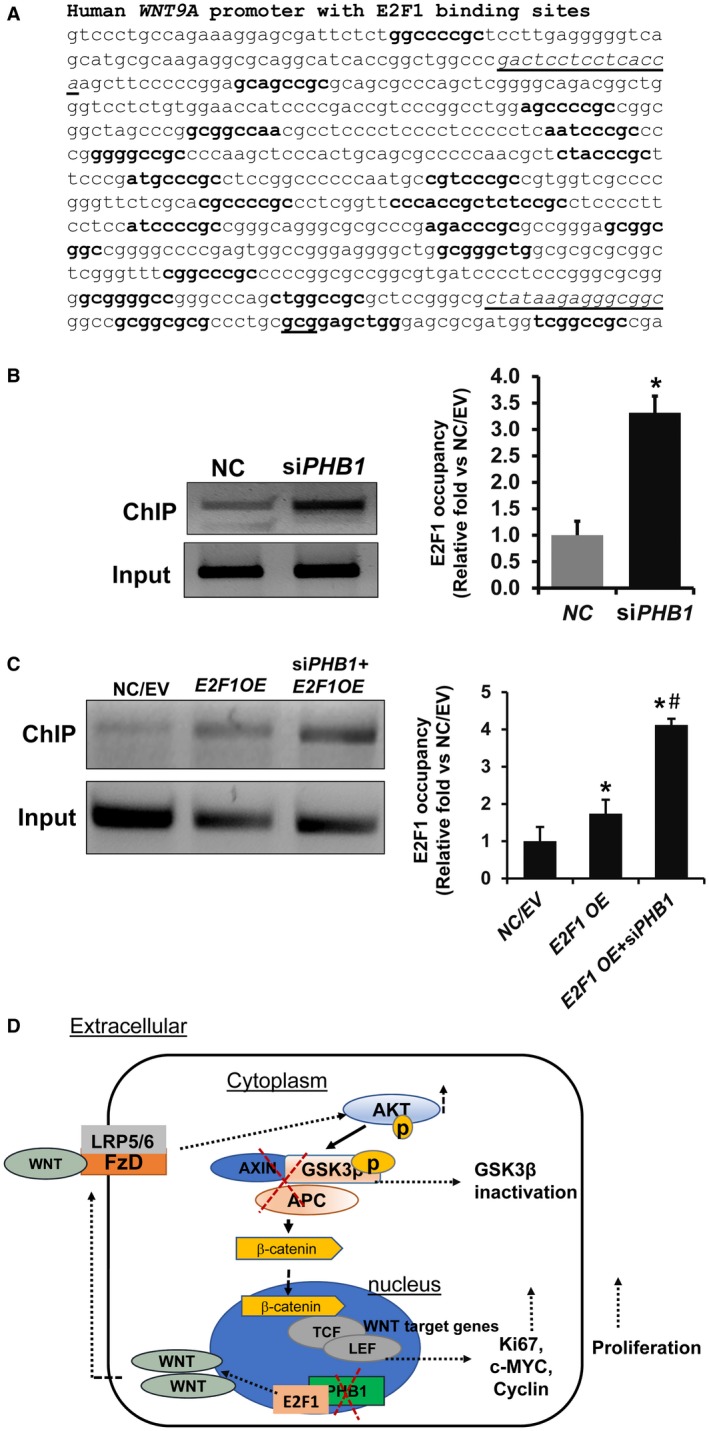
PHB1 silencing leads to increased E2F1 binding to the WNT9A promoter in HepG2 cells. (A) Predicted E2F1 binding sites (in bold) in the human WNT9A (Accession ID, HM015601.1) sequence was determined by ALGGEN PROMO transcription factor bindings prediction software. Transcription start site is gcg underlined in bold. Sequences that are underlined are primer sequences used for the ChIP assay. (B) E2F1 binding to the WNT9A promoter was determined by ChIP assay. Chromatin was prepared from NC and PHB1‐silenced HepG2 cells, and ChIP assay was performed as described in Materials and Methods. Relative target site occupancy is represented as fold over NC. Results represent mean ± SEM from three independent experiments in duplicates; *P < 0.05 versus NC. (C) Effect of E2F1 OE for 48 hours in conjunction with 72 hours of PHB1 silencing on E2F1 binding to the WNT9A promoter in HepG2 cells. Results represent mean ± SEM from three to six independent experiments in duplicates; *P < 0.05 versus NC/EV, #P < 0.05 E2F1 OE versus E2F1 OE+siPHB1. (D) Summary demonstrating the potential role of PHB1 in modulating WNT signaling in Phb1 KO livers and HepG2 cells. PHB1 deletion leads to induction of WNT ligands in an E2F1‐dependent manner. WNT ligands induce downstream activation of WNT‐beta‐catenin signaling through the AKT‐GSK3beta signaling pathway. This results in increased TCF transcriptional activity and cell proliferation. Abbreviations: APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; c‐MYC, Myc Proto‐Oncogene; FzD, Frizzled.
