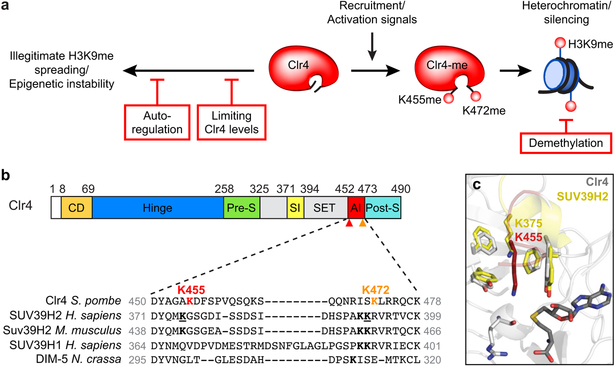
Extended Data Figure 10 ∣. Clr4 automethylation-dependent heterochromatin regulation and evidence for its evolutionary conservation.
a, Schematic summary of the role of AI loop lysine automethylation in preventing illegitimate heterochromatin formation and epigenetic instability (left). Intrinsic regulation of Clr4 by automethylation (K455 and likely K472) acts in parallel with other anti-silencing mechanisms involving regulation of Clr4 levels and H3K9 demethylation (red boxes). See main text for additional discussion. b, Top, diagram illustrating the domain organization of the S. pombe Clr4 protein and the location of Clr4 K455 (red arrowhead) and K472 (orange arrowhead). Bottom, sequence alignment of Clr4 AI loop containing K455 (red) and K472 (orange) in the indicated methyltransferases. SUV39H2-K375 and SUV39H2-K392 are indicated in underlined bold. H. sapiens, Homo sapiens; M. musculus, Mus musculus; N. crassa, Neurospora crassa. c, Overlay of S. pombe Clr4 in grey (this study, PDB ID 6BOX) and human SUV39H2 in yellow (PDB ID 2R3A) showing that S. pombe Clr4-K455 (shown as red stick) and human SUV39H2-K375 (shown as yellow stick) occupy partially overlapping positions inside the catalytic pocket.