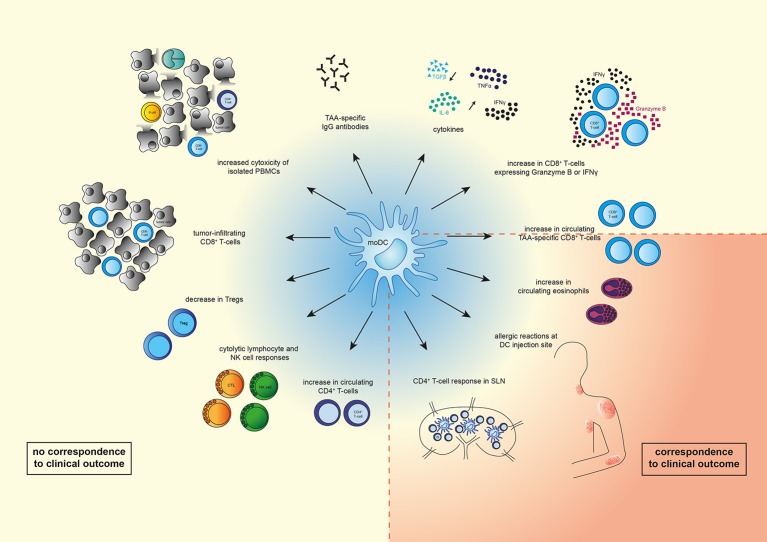
Figure 1.
Overview of immunological changes observed upon moDC therapy. Vaccination with moDCs can lead to various immunological changes such as an increase in numbers of circulating immune cells (TAA-specific CD8+ T-cells, CD8+ T-cells expressing IFNγ or Granzyme B, CD4+ T-cells, eosinophils), or a decrease of other immune cells (Tregs). In addition, systemic cytolytic lymphocyte (CTL) or natural killer (NK) cell responses, as well as CD4+ T-cell responses in sentinel lymph nodes (LNs) were observed. Levels of TAA-specific IgG antibodies and cytokines (IL-6, IFNγ, TNFα) increased, whereas levels of TGFβ decreased. Vaccination with moDCs also resulted in tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T-cells, increased cytotoxicity of isolated PBMCs (monocytes, CD8+ and CD4+ T-cells, B-cells), and allergic reactions at the DC injection site. Of the shown changes, only increased circulating TAA-specific CD8+ T-cells, eosinophilic blood count, strength of allergic reactions at DC injection site, and a CD4+ T-cell response in sentinel LNs correspond to clinical outcome.