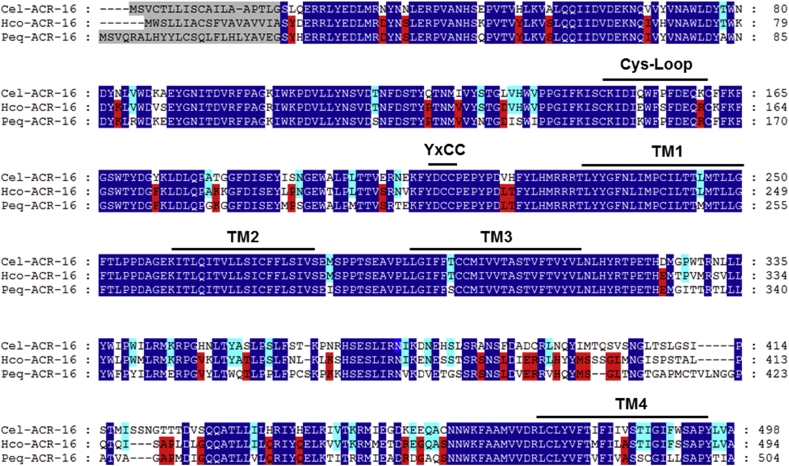
Fig. 5.
Amino-acid alignments of ACR-16 subunit sequences from Caenorhabditis elegans, Haemonchus contortus and Parascaris equorum. acr-16 deduced amino-acid sequences were aligned using the MUSCLE algorithm (Edgar, 2004) and further processed using GeneDoc. Predicted signal peptide sequences are shaded in grey. Amino acids conserved between all the ACR-16 sequences are highlighted in dark blue. Amino acids specifically shared by ACR-16 homologs from parasitic species are highlighted in red. Amino acids specifically shared by Clade V nematode species (C. elegans and H. contortus) are highlighted in light blue. The cys-loop, the four transmembrane regions (TM1–TM4) and the primary agonist binding (YxCC) are indicated above the sequences. Cel (Caenorhabditis elegans), Hco (Haemonchus contortus), Peq (Parascaris equorum). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)