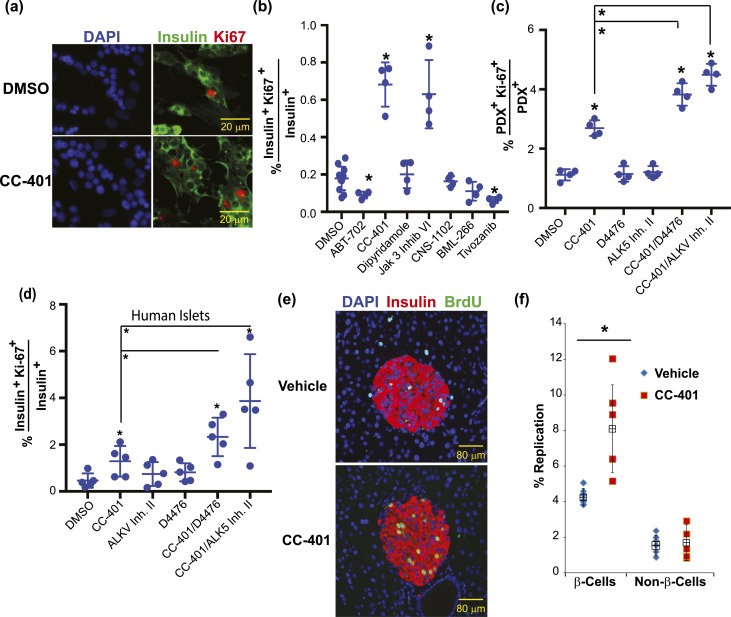
Figure 2.
CC-401 stimulates human β-cell replication in vitro and mouse β-cell replication in vivo. (a) Representative immunofluorescence images of vehicle- (DMSO) and CC-401–treated human islet cultures [DAPI (blue); insulin (green)]. (b) The β-cell–replication index of dispersed human islet cultures after compound treatment (48 hours). Independent treatments along with mean ± standard deviation (SD) are shown. *P < 0.05. Similar data were obtained from at least five independent islet procurements. (c) Rat β-cell–replication index of compound-treated (CC-401, 10 µM; D4476, 5 µM; and ALK5 inhibitor II, 2 µM) primary islet cultures. Independent replicates (n = 4) are shown with mean ± SD. *P < 0.01; >1000 β cells counted per data point. (d) Human β-cell–replication index of compound-treated islet cultures. Independent replicates (n = 5) are shown with mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; >1000 β cells counted per data point. (e) Representative images of pancreatic sections from 8-week female vehicle- and CC-401–treated mice stained for insulin (red), BrdU (green), and nuclei (blue). See Supplemental Fig. 2 for determination of CC-401’s in vivo half-life and in vitro potency. (f) The BrdU incorporation index (percentage of replication) of β cells (insulin+) and non–β cells (insulin−) after treatment with vehicle or CC-401 (25 mg/kg) for 1 week. Data from individual mice (n = 5) and mean ± SD shown. *P < 0.05. Error bars represent the standard deviation of an experimental condition (n ≥ 3). Two independent experiments were performed with similar results. See Supplemental Fig. 2 for in vitro replication effects on α cells, δ cells, and dermal fibroblasts. ALKV Inh. II, activin A receptor type II–like kinase inhibitor II.