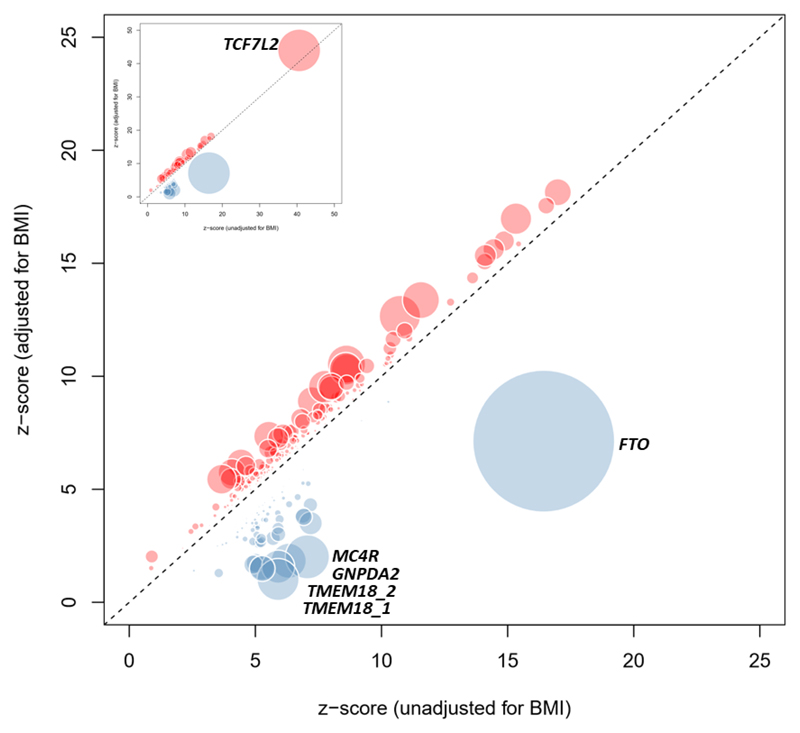
Figure 2. Comparison of estimated T2D effect size between BMI-adjusted and unadjusted models.
Z-score for each of the 403 distinct signals from BMI-unadjusted analysis (50,791 cases and 526,121 controls; x-axis) is plotted against the z-score from the BMI-adjusted analysis (50,402 cases and 523,888 controls; y-axis). Variants that display higher T2D effect size in BMI-adjusted analysis are shown in red and variants with higher T2D effects in BMI-unadjusted analysis are shown in blue. Diameter of the circle is proportional to -log10 heterogeneity p-value.