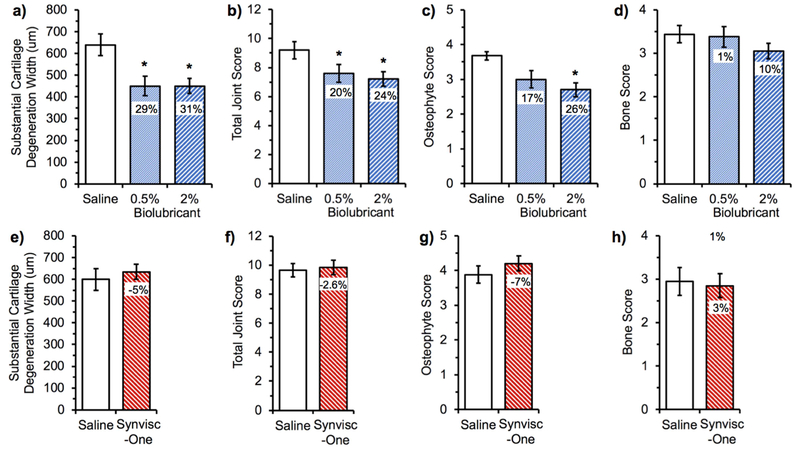
Figure 6.
Summary of histological evaluation of rat knee joints exposed to different treatments following medial meniscal tear. One week after inducing the tear, the knees were intra-articularly injected with either the biolubricant (0.5 wt% or 2 wt%), saline, or Synvisc-One® and were harvested 3 weeks later for histological analysis. Effect of the biolubricant vs. saline (a, b, c and d) at two different concentrations (0.5 and 2 wt/v%). Effect of Synvisc-One® vs. saline (e, f, g and h). The differences (in percent) were standardized against the saline control. *P<0.05 vs. saline control, n=20 per group. Baseline healthy values for an animal not receiving the medial meniscal tear nor treatment via intra-articular injection for each endpoint are as follows: Substantial cartilage degeneration width (a, e), 0 μ m; total joint score (b, f), 1; osteophyte score (c, g), 1; and bone score (d, h), 0.[34]