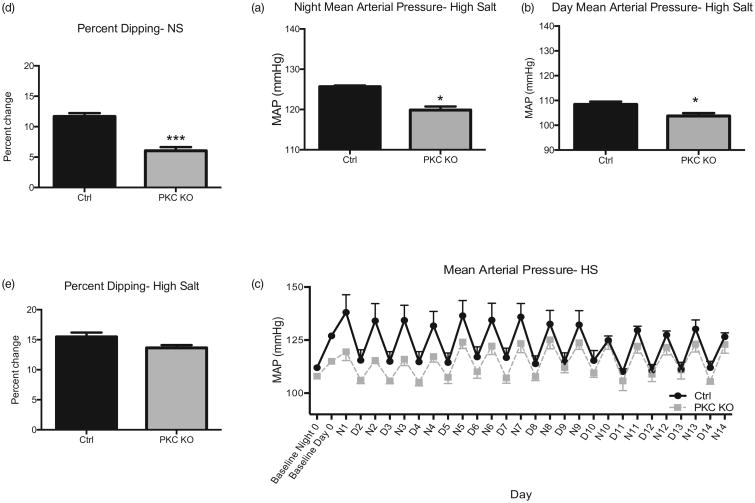
Figure 3.
Protein kinase Cα knock out mice have reduced resting phase dipping blood pressure response. Mice were then fed a high salt diet (4%) for 14 days. Blood pressure responses were averaged at the end of the 14 day period for both night (a) and day (b) period. Daily mean arterial pressures following high salt (4%) chow feeding are shown (c) from baseline period. Baseline night and day measurements are averaged from previous recording period. To determine resting phase dipping blood pressure, mean arterial pressure is presented as a percentage change from night (awake) mean arterial pressures during both normal chow (d) and high salt (14 days) (e) feedings. Representative traces are shown for high salt (d) periods, with average baseline night/day blood pressure. Data shown as mean±SEM, n = 4–5, ***P < 0.001