Fig. 1.
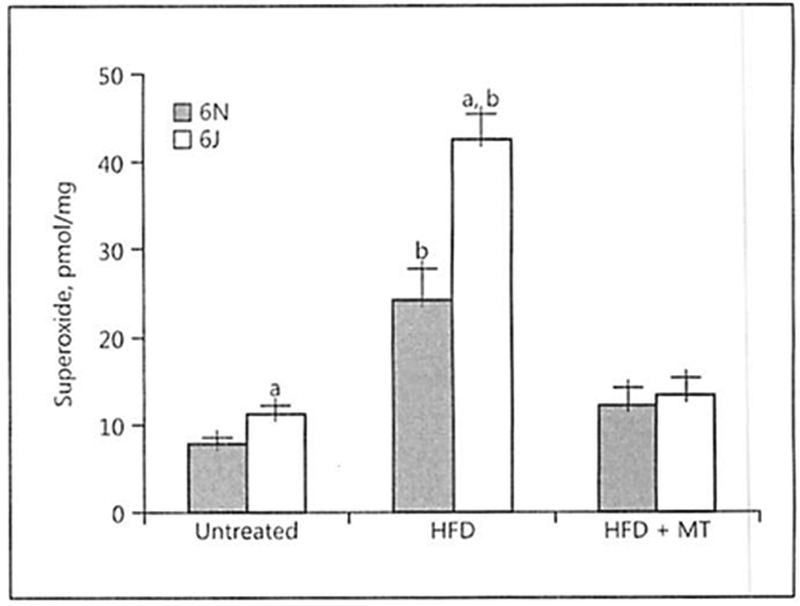
High-fat diet (HFD) exacerbates the increased vascular superoxide production observed in C57BL/6J mice. Vascular superoxide production was determined in untreated mice, those with AAV8-PCSK9 virus (3 × 1010 vector genomes) for 2 weeks and then subjected to HFD for 8 weeks, or HFD for 4 weeks followed by co-treatment with HFD and MitoTEMPO (MT; 0.8 mg/kg/day) for the final 4 weeks of the experiment. Superoxide was quantified in the left carotid sinus of the mice by exposing the animals to dihydroethidium at 10 mg/kg i.p. for 1 h and measuring the superoxide-specific oxidation product 2-OH-HE+ by HPLC. Values are means ± SEM of ≥6–8 animals. a p < 0.05 versus 6N; b p < 0.05 versus untreated.
