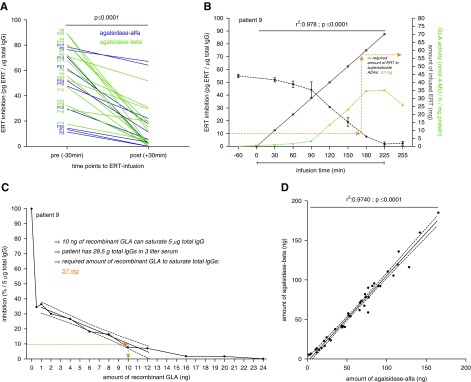
Figure 1.
The required amount of recombinant enzyme for antibody saturation can be calculated using patients' purified total IgGs. (A) Determination of the individual antibody status before and after infusion. (B) Effect of infused ERT amounts (gray) on antibody titer (black) during infusion and agalsidase activity (green). The longitudinal measurement of ADA titers during infusions allows estimating the amount of enzyme required to saturate ADAs. (C) Titration of purified total IgG against ERT allows calculating the required amount of enzyme from one serum sample. The determination of the individual amount of recombinant GLA to saturate ADAs was performed using titration and subsequent calculation. First, a titration was performed to identify the required amount of enzyme to saturate 90% of 5 µg total IgGs (see Methods). ERT inhibition was plotted against the amount of enzyme. The amount required can be identified on the y-axis (here 10 ng, dashed orange line), showing that 2 ng is sufficient to saturate 1 µg total IgG. In the example shown, the patient’s measured IgG concentration was 9.5 mg/ml serum. Because each patient has approximately 3 L of serum, the total amount of patient’s IgGs per total volume of serum was calculated with 28.5 g. Therefore, the amount of enzyme required to saturate 90% of all IgGs was 57 mg (28.5 g×2/1000=57 mg). (D) Crosstitration of agalsidase-α and agalsidase-β demonstrates similar ADA saturation of either type of enzyme.