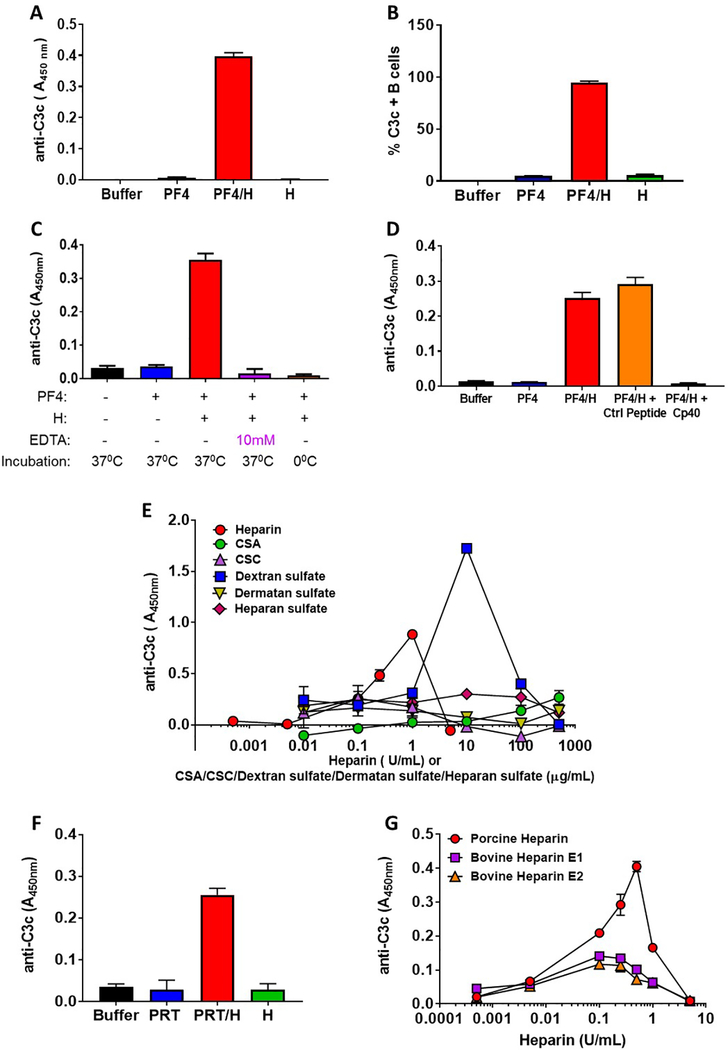
Figure 1:
(A) Antigen-C3 capture immunoassay detects complement activation by PF4/heparin complexes in plasma. Plasma from a healthy donor was incubated with buffer or antigen (PF4, 25μg/mL ± heparin 0.25 U/mL) or heparin alone (0.25 U/mL) and binding of C3c was determined by ELISA as described in supplemental methods. The bar graph shows the anti-C3c absorbance in different incubation conditions. (B) Flow-based method for complement activation by PF4/heparin complexes. Whole blood from a healthy donor was incubated with buffer or antigen (PF4, 25μg/mL ± heparin, 0.25 U/mL) or heparin alone (0.25 U/mL) and the binding of C3c to the B cells was determined by flow cytometry. The bar graph shows the % of C3c-positive B cells in different incubation conditions (C) Antigen-C3c immunoassay is sensitive to complement inhibition. Plasma from a healthy donor was incubated with buffer or antigen (PF4, 25 μg/mL ± heparin 0.25 U/mL) in presence or absence of 10 mM EDTA for 60 minutes at 37° C or 0°C and the binding of C3c to the complexes was determined by ELISA with a KKO coated plate. The bar graph shows the anti-C3c absorbance in different conditions. (D) Peptide C3 inhibitor Cp40 inhibits complement activation by PF4/heparin complexes. Plasma from a healthy donor was incubated with buffer or antigen (PF4, 25μg/mL ± heparin 0.25 U/mL) in the presence or absence of 5 μM Cp40 or Control (Ctrl) peptide and binding of C3c was determined by ELISA with a KKO coated plate. The bar graph shows the anti-C3c absorbance in different incubation conditions. (E) Complement activation by PF4-UFH and PF4/GAGs. Plasma from a healthy donor was incubated with fixed does of PF4 (25 μg/mL) and varying doses of UFH (0.0005–5.0 U/mL) or GAGs (0.01–500 μg/mL) and the binding of C3c to the PF4/heparin or PF4/GAGs complexes was determined by ELISA as described in supplemental methods. The graph shows the anti C3c absorbance at different concentrations of UFH or different GAGs. (F) Detection of complement activation by PRT/heparin complexes. Plasma from a healthy donor was incubated with buffer or PRT ( 100 μg/mL ) ± heparin (10 U/mL) or heparin alone (10 U/mL) and binding of C3c was determined by ELISA on an anti-PRT/heparin antibody (ADA) coated plate. The bar graph shows the anti C3c absorbance in different incubation conditions. (G) Comparison of complement activation by porcine and bovine (E1 and E2) UFH. Plasma from a healthy donor was incubated with fixed does of PF4 (25 μg/mL) and varying doses of porcine or bovine UFH (0.0005– 5 U/mL) and the binding of C3c to the PF4/heparin complexes was determined by ELISA with a KKO coated plate. The graph shows the anti C3c binding at different concentrations of porcine/bovine UFH.