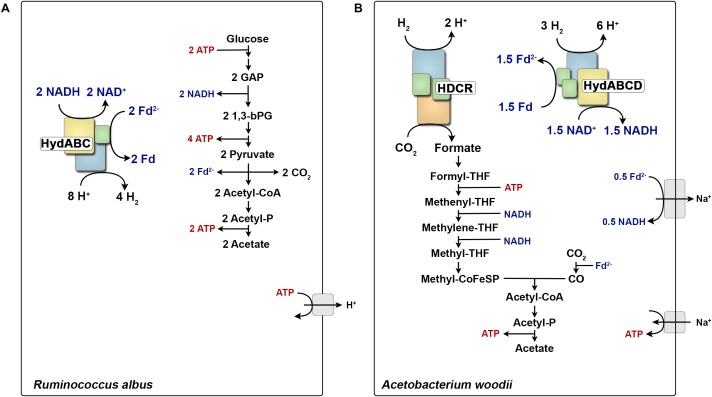
FIGURE 1.
Role of multimeric hydrogenases in the energy metabolism of Ruminococcus albus (A) and Acetobacterium woodii (B). During glucose fermentation, R. albus oxidizes glucose to two molecules acetate. All generated reducing equivalents are reoxidized by the electron confurcating hydrogenase HydABC. In contrast, A. woodii can grow with H2 + CO2 as substrates and forms acetate as major end product. HDCR catalyzes the first step of the WLP from CO2 to formate. All reducing equivalents are provided from H2 oxidation catalyzed by the electron bifurcating hydrogenase HydABCD. Fd2-, reduced ferredoxin; CoA, coenzyme-A; THF, tetrahydrofolate; CoFeSP, corrinoid–iron–sulfur protein; GAP, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate; 1,3-bPG, 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate.