FIGURE 1.
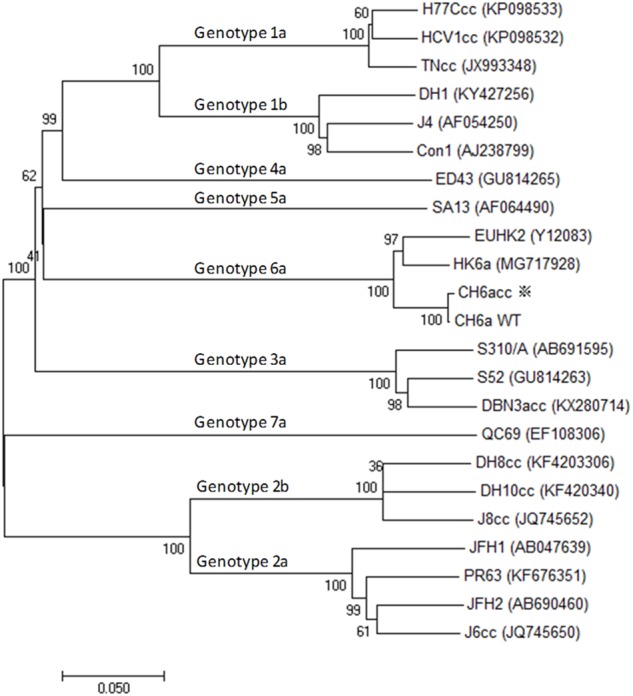
Phylogenetic analysis of CH6a and other HCV isolates of genotypes 1–7. Phylogenetic analysis of ORF nucleotide sequences of CH6a wild-type (WT) and CH6acc (asterisk), as well as other HCV isolates representative of the advanced cell culture systems of respective genotype, including cell culture infectious full-length clones and those full-length sequences that are not infectious in vitro. The available culture infectious full-length HCV clones are 1a (TNcc, HCV1cc, and H77Ccc) (Li et al., 2012b; Li et al., 2015b), 2a (JFH1, J6cc, PR63, and JFH2) (Wakita et al., 2005; Date et al., 2012; Li et al., 2012a; Lu et al., 2014), 2b (J8cc, DH8cc, and DH10cc) (Ramirez et al., 2014), 3a (DBN3acc) (Ramirez et al., 2016), and 6a [recently published HK6acc (Pham et al., 2018), as well as CH6acc reported in this study]. Full-length sequence includes 1b (Con1, J4, and DH1), 3a (S52), 4a (ED43) and 5a (SA13), and 7a (QC69) (Gottwein et al., 2009; Li Y.P. et al., 2014; Pham et al., 2017; Li et al., 2018). The evolutionary history was inferred by using the neighbor-joining method in the freeware Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA), version 7 (Kumar et al., 2016).
