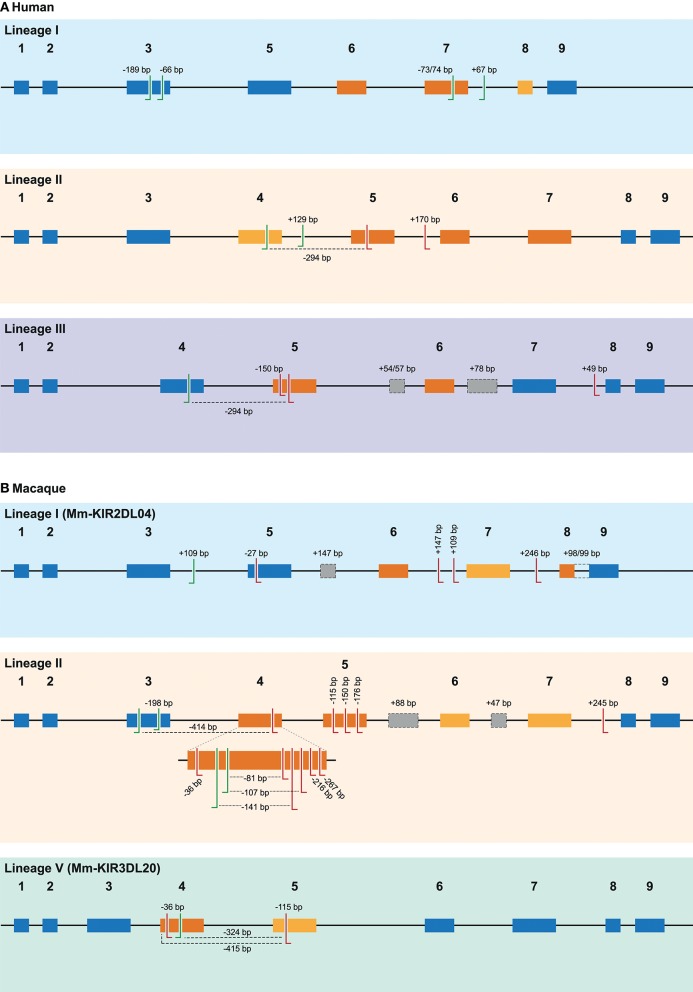
Figure 2.
Overview of alternative splice sites in human and rhesus macaque KIR. A schematic representation of the different splice events observed in human (A) and rhesus macaque (B) KIR transcripts categorized by gene lineage. The splice events illustrated correspond to the splice events summarized in Tables 1, 2, and are indicated with the size of the inclusion (+) or deletion (–) in base pairs (bp), or by color-coding. The black line indicates the introns, whereas colored boxes represent the exons. Exons that are subjected to exon skipping are illustrated with dark orange boxes, and the exons that are only skipped in combination with one or more exons are indicated in light orange boxes. Exons that are not subjected to exon skipping are colored blue. The actual splice sites, which map to the exon/intron boundaries, have not been indicated. Alternative 3′ splice sites (ss) are indicated with green left-directed hooks, whereas alternative 5′ ss are indicated with red right-directed hooks. An alternative splice site always pair with the adjunct complement actual 3′ or 5′ splice site, except splice events that are mediated by a set of 3′ and 5′ alternative ss, which are marked with a dashed line. Cryptic exons are illustrated as gray boxes with a dashed line, and the (alternative) splice sites of these cryptic exons are not explicitly indicated. The intron retention event observed in rhesus macaque KIR2DL04 (lineage I) is indicated with a dashed line between exons 8 and 9. Exon 4 in rhesus macaque lineage II KIR genes is enlarged to more precisely illustrate the high number of alternative splice events observed.