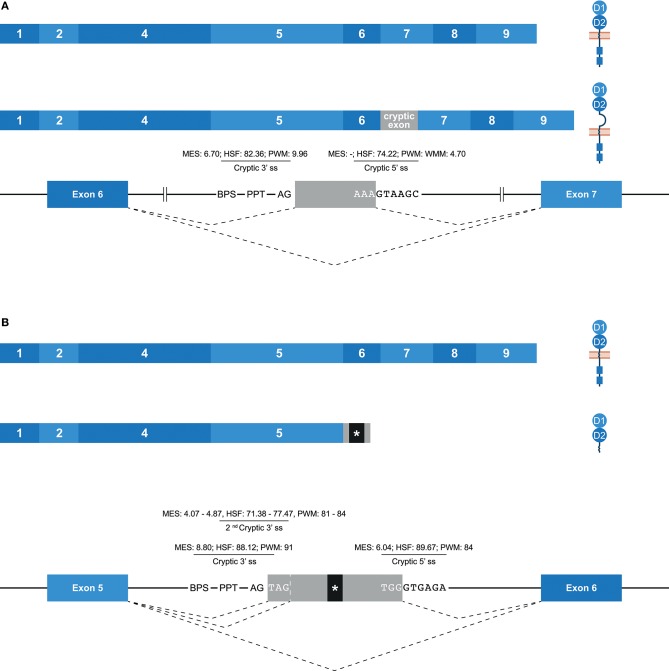
Figure 6.
Inclusion of cryptic exons by alternative splicing. The observed transcripts are illustrated, in which exons are indicated by blue boxes, and corresponding protein structures are schematically depicted adjacent to the transcript. Cryptic exons are indicated in gray boxes. Dashed lines indicate the potential splice events, and predicted splicing strength scores are provided for cryptic splice sites. Stopcodons are indicated by black boxes with an asterisk (*). (A) In transcripts of KIR2DL1-3/2DS1, a cryptic exon of 78 bp was observed that originated from intron 6. This inclusion extends the region between the stem and transmembrane region by 26 amino acids, including positively and negatively charged residues. (B) In transcripts of KIR2DL1 and KIR2DS5, a cryptic exon of 57 bp was observed, which originated from intron 5. Three bp upstream, a second cryptic 3′ ss was identified, which explained the cryptic exon inclusion of 54 bp in transcripts of KIR2DS1 and KIR2DS4. At the gDNA level, the presence of one or both of these cryptic exons was also identified in other lineage III KIR genes and KIR2DL5.