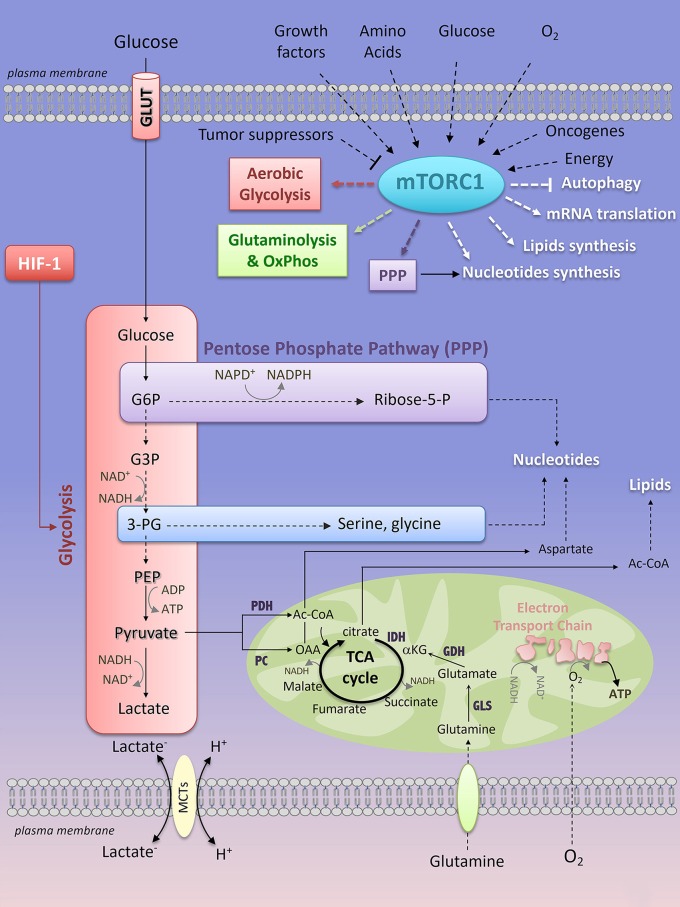
Figure 2.
Key interconnected metabolic pathways and their relevance to mTORC1 activation. Extrinsic (growth factors, amino acids, oxygen, glucose) and intrinsic (oncogene, energy levels) factors activate mTORC1 signaling, while tumor suppressors prevent its activation. In turn, mTORC1 enhances glycolysis, through HIF-1-dependent glycolytic program, the pentose phosphate pathway, and glutamine metabolism. mTORC1-dependent regulation of cell metabolism converges through an anabolic program resulting in increased nucleotides, protein and lipid synthesis while inhibiting autophagy. mTORC1, mTOR complex 1; PPP, pentose phosphate pathway; HIF-1, Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; PC, pyruvate carboxylase; IDH, isocitrate dehydrogenase; GDH, glutamate dehydrogenase; GLS, glutaminase; Ac-CoA, Acetyl-CoA; OAA, oxaloacetate; α-KG, α-ketoglutarate; G6P, glucose-6-phosphate; G3P, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; 3-PG, 3-phosphoglycerate; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; Ribose-5-P, Ribose-5-phosphate; ADP, adenosine diphosphate; ATP, adenosine 5′-triphosphate; NAD+, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NADH, reduced form of NAD+; NADP+, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NADPH, reduced form of NADP+.