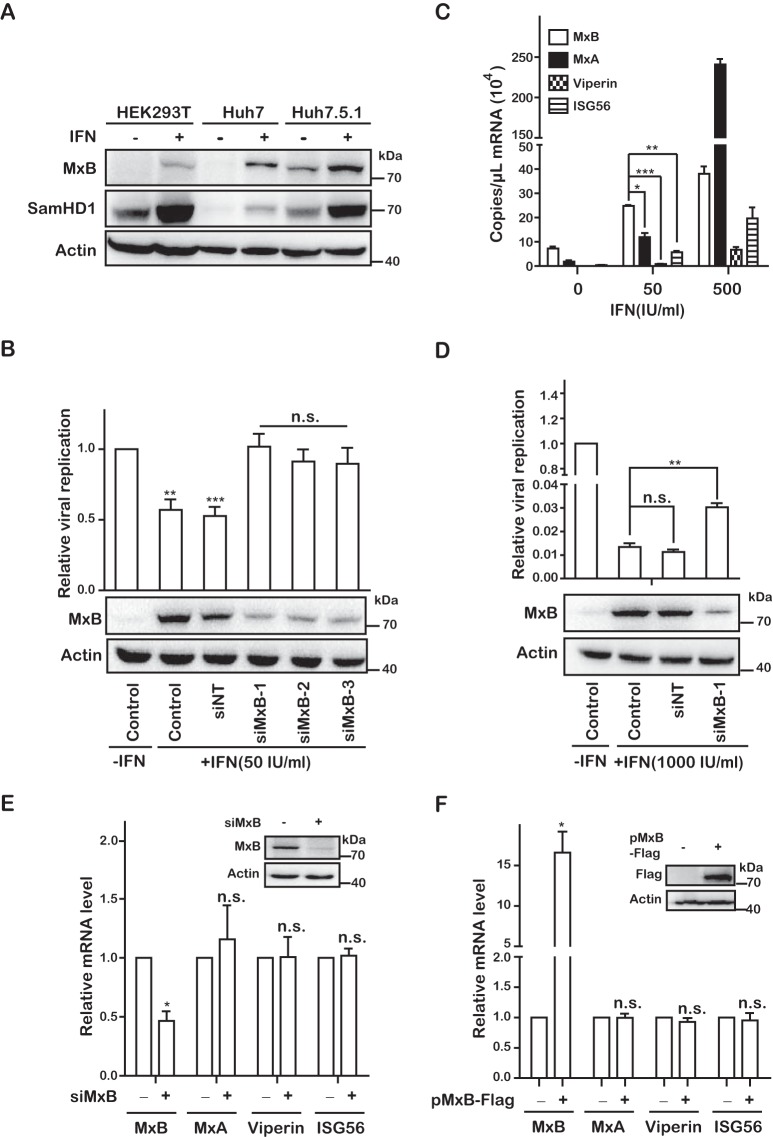
FIG 2.
MxB plays an important role in IFN-mediated inhibition of HCV infection. (A) Expression levels of MxB in different cell lines. HEK293T, Huh7, and Huh7.5.1 cells were treated with IFN-α-2b (500 IU/ml) for 48 h. Levels of MxB and SamHD1 were determined by Western blotting. (B and D) Jc1 HCVcc was used to infect Huh7 cells that were transfected with either siRNA targeting MxB or control scrambled siRNA (siNT), followed by treatment with 50 IU/ml IFN-α-2b (B) or 1,000 IU/ml IFN-α-2b (D). Levels of MxB were determined by Western blotting. HCV infection was assessed by measuring Gluc activity at 72 hpi. (C) Huh7 cells were treated with IFN-α-2b (0, 50, and 500 IU/ml) for 48 h. The mRNA copies of MxB, MxA, Viperin, and ISG56 were quantified by qRT-PCR. (E) Huh7 cells were transfected with either siRNA targeting MxB or control scrambled siRNA (siNT) and treated with 50 IU/ml IFN-α-2b for 48 h, and mRNA levels of MxB, MxA, Viperin, and ISG56 were detected by qRT-PCR. (F) Huh7 cells were transfected with a plasmid expressing MxB-Flag for 48 h, and mRNA levels of MxB, MxA, Viperin, and ISG56 were detected by qRT-PCR. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments, and values are expressed as means ± SD. For panels B and D to F, data are normalized to the control group, with the control value arbitrarily set to 1.