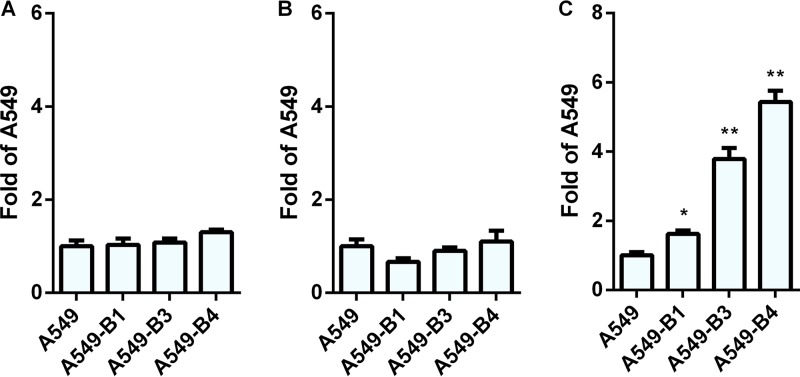
FIG 14.
Binding, internalization, and transduction efficiencies of HAdV26 in A549 cell clones with increased expression of β3 integrin. (A and B) Binding (A) and internalization (B) of HAdV26 in A549 cells and A549 cell clones with increased expression of β3 integrin (A549-B1, A549-B3, and A549-B4). Cells were incubated with HAdV26 on ice for 1 h at an MOI of 1,000 vp/cell. To measure binding, unbound viruses were removed by rinsing the cells with cold trypsin and PBS and collected by scraping the cells. For internalization measurement, unbound viruses were removed as described above, and the cells were transferred to 37°C and incubated for 1 h, allowing the viruses to enter the cells. The cells were then rinsed twice with warm trypsin, dispersed, and pelleted by centrifugation. For both binding and internalization, total (cellular plus viral) DNA was extracted from cells and used for quantification of viral DNA by qPCR, using the CMV region as a target sequence. The results are expressed as fold value obtained for A549 cells plus standard deviations. (C) Transduction efficiencies of HAdV26 in A549 cells and A549 cell clones with increased expression of β3 integrin (A549-B1, A549-B3, and A549-B4). Transduction efficiency was measured by flow cytometry 48 h after infection. The results are expressed as fold value obtained for A549 cells plus standard deviations. *, P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01. Results are from three independent experiments (n = 3).