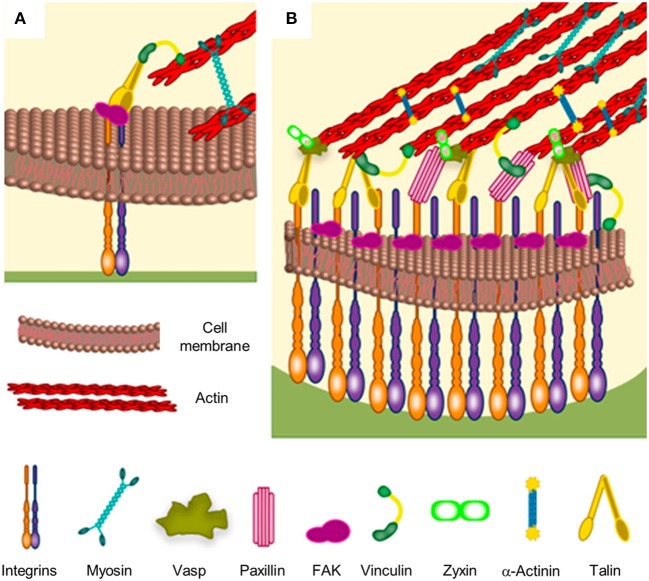
Figure 1.
Schematic of focal adhesion formation and maturation. (A) Nascent adhesions are thought to form the binding of integrins to extracellular ligands. Additional cytoplasmic components, such as talin, FAK and paxillin are recruited to stabilize the ligand-bound clusters. Myosin-generated forces promote conformational changes of talin, which exposes binding sites for vinculin. Stable clusters can grow further by addition of other integrins and cytoplasmic molecules, thus generating a focal complex and then a focal adhesion. (B) The multi-layered structure of a mature focal adhesion comprises proteins with different functions: signaling (integrins, FAK, and paxillin), force transduction (vinculin and talin) and linkers to the cytoskeleton (Vasp, zyxin, and α-actinin). Reprinted with permission from Ventre and Netti (2016b). Copyright 2016 American Chemical Society.