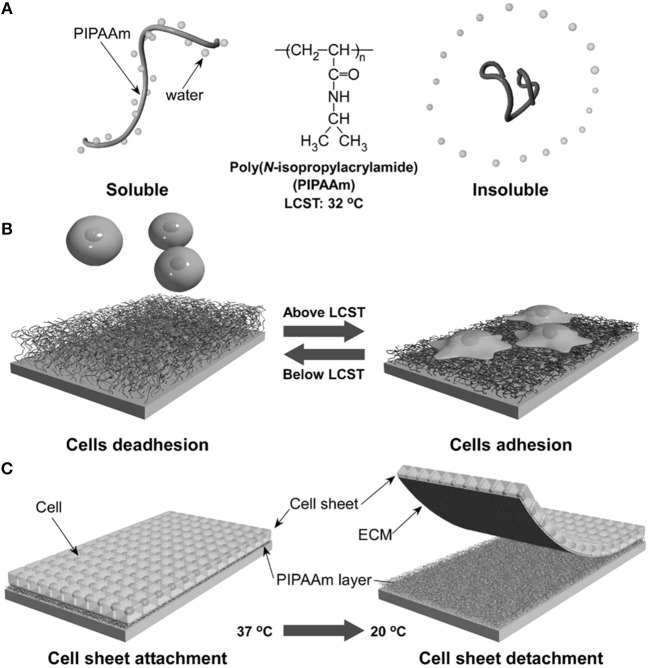
Figure 7.
Schematic illustration of the temperature-responsive behavior of PNIPAM. In aqueous solution and above LCST, PNIPAM is stabilized by hydrophobic interactions excluding water (A). This causes FN adsorption and cell adhesion. Conversely cooling below the LCST promotes water inflow and FN release with consequent cell detachment (B). Confluent layers of adhering cells can detach from PNIPAM-grafted substrates when decreasing temperature from 37 to 20°C (C). Reprinted from Tang and Okano (2014).