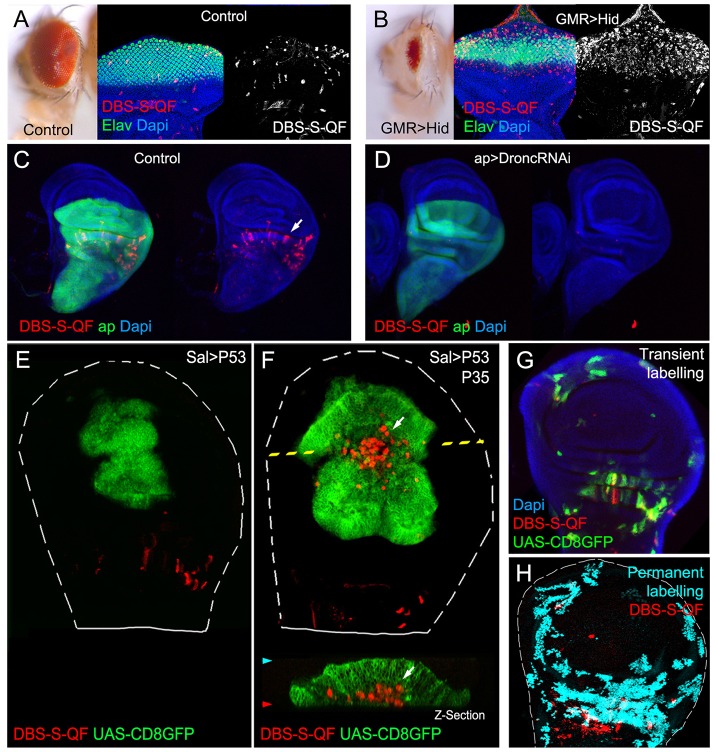
Fig. 4.
Functional characterisation of the DBS-S-QF sensor. (A,B) Activation of the DBS-S-QF reporter in either wild-type (A) or apoptotic eyes ectopically expressing Hid under the regulation of GMR promoter (B). Adult eyes and imaginal discs are shown on the left and right panels, respectively. Activation of DBS-S-QF is shown in red upon induction of a QUAS-Tomato-HA transgene (anti-HA in red). Differentiated regions of the eye express the neuronal identity marker Elav (green); nuclei are labelled with DAPI. (C) Activation of DBS-S-QF (anti-HA in red; white arrow) in a wild-type wing disc expressing CD8-GFP (UAS-CD8-GFP) under the regulation of apterous-Gal4 (green); the experiment was carried out at 29°C. (D) Activation of DBS-S-QF (anti-HA in red) in a wing disc expressing a RNA interference against Dronc (UAS-Dronc-RNAi) and CD8-GFP under the regulation of apterous-Gal4 (green); the experiment was performed at 29°C. (E) Overexpression of P53 and CD8-GFP under the regulation of spalt-Gal4 (green); red channel shows the DBS-S-QF activation (QUAS-Tomato-HA, anti-HA in red). Notice the absence of Tomato expression in the GFP-expressing cells. The dashed white line outlines the wing disc. (F) Co-expression of P53, P35 and CD8-GFP in the spalt-Gal4 expression domain (green); red channel shows the DBS-S-QF activation (QUAS-Tomato-HA, anti-HA in red); white arrow in xy-image or z-section indicates the appearance of ‘undead cells’ basally delaminated (‘undead cells’ refers to caspase-activating cells that cannot finalise the apoptosis programme owing to the presence of P35 blocking the activation of the effector caspases). (G) Temporal perspective of caspase-activating cells in a wild-type wing disc using transient fluorescent markers expressed under the control of DBS-S-QF; QUAS-Tomato-HA (anti-HA in red) labels ongoing caspase activation; old caspase activation is shown in green (QUAS-Gal4 UAS-mCD8-GFP); recent-past caspase activation is indicated by the colocalisation of both markers (yellow); DAPI labels nuclei. (H) Lineage tracing of caspase-activating cells in a wild-type wing disc obtained with DBS-S-QF (ongoing activation of DBS-S-QF is shown in red; nuclear β-gal staining shows in cyan the permanent labelling of caspase-activating cells).