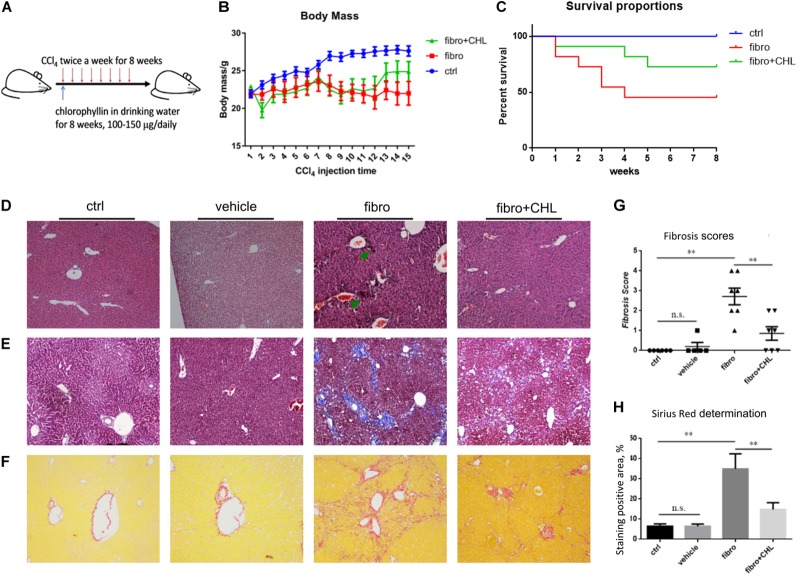
FIGURE 1.
CCl4 induced liver fibrosis in mice is ameliorated by oral administration of chlorophyllin. BALB/c male mice were randomly divided into three groups: control, fibrosis, fibrosis treated with chlorophyllin (n = 6 and repeating twice). Liver fibrosis of the mice was induced via intraperitoneal injection of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) for 8 weeks. Oral administration of chlorophyllin was conducted by adding to drinking water at a dose of 25 μg/mL (equivalent 5 mg/kg body mass). (A) Sketch of the experimental design. (B) Changing body mass. (C) Survival rate. (D) Hematoxylin and Eosin staining of the liver tissues. (E) Masson’s Trichrome staining for liver fibrosis. (F) Sirius Red staining for liver fibrosis. (G) Fibrosis scores have been determined with pathologists in a blind manner. (H) Semi-quantitative determination of fibrosis stained by Sirius Red. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01. ∗/∗∗ Comparisons have been indicated with bars. Data show Means ± SEM.