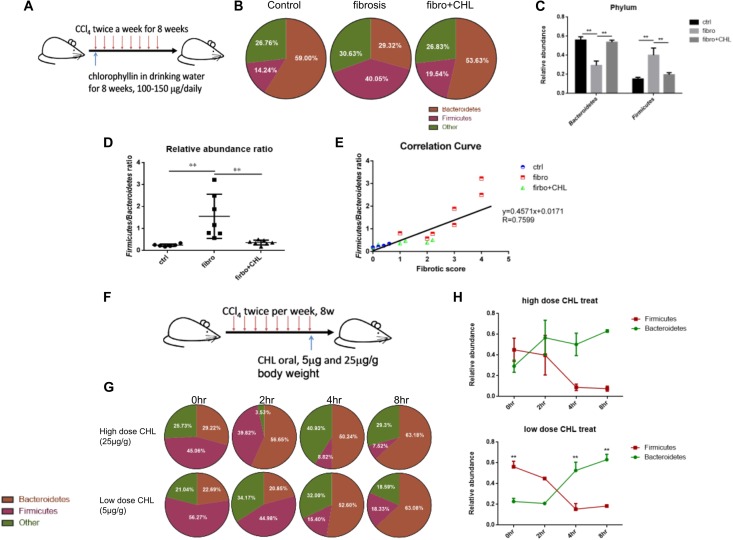
FIGURE 6.
Dysbiosis occurring in the liver fibrosis can be rebalanced by oral administration of chlorophyllin for eubiosis. (A) Sketch of the experimental design. (B–E) The fecal microbiome of mice as described in Figure 1 was measured via 16S rDNA-qPCR analysis. Relative abundance of Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes in the three conditions was shown and related to endotoxin in plasma, consequently reduced hepatic inflammation and fibrogenesis. (F–H) Acute impact of oral administration of chlorophyllin on the gut microbiota. Liver fibrotic mice received two doses of chlorophyllin through oral gavage, at 5 and 25 μg/g, respectively. Feces were collected at the indicated time points for 16S rDNA-qPCR analysis. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01. ∗/∗∗ Comparisons have been indicated with bars. Data show Means ± SEM.